Page 219 - 2021_05-Haematologica-web
P. 219
2'-O-methoxyethyl splice-switching oligos
with the b-sickle allele. There are limited epidemiological studies on the b-sickle/b-thalassemia genotype, however the literature indicates their clinical presentation as severe.29 Clinical complications seen in patients with b- sickle/b-thalassemia genotype are mainly due to the large relative quantity of HbS that is present, given the b-tha- lassemia allele does not produce enough HbA. As we could not obtain a sample with the compound IVS2- 745/b-S genotype, we artificially created a model system, by transducing two homozygous sickle specimens (S1 and S2) with an erythroid-specific lentiviral vector, AnkCT9W-745, that carries an IVS2-745 HBB transgene.
We analyzed integration of transduced S1 and S2 cells and detected a VCN of 2.02 and 1.62, respectively, which replicates a somewhat “heterozygous” state, as the two endogenous sickle alleles were matched by roughly two IVS2-745 alleles in each specimen. Upon differentiation and exposure to hypoxia, S1 scramble-treated cells showed prong-like polymers of sickle chains. 2'-MOE- SSO 91 treatment of S1 resulted in an increase in HbA from 8.96±1.88% to 59.82±0.23%, and a decrease in HbS, from 75.34±2.33% to 30.73±0.32% (Figure 8A). This increase in HbA proportion at the expense of HbS led to a 50% reduction in the sickling effect. Following treatment,
A
B
C
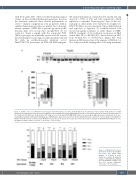
Figure 5. Additive effect of 2'-MOE-SSO in homozygous IVS2-745 patient cells (P5). (A) Electrophoresis of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products of cDNA obtained from erythroblasts from specimen P5. Wild-type (WT) and IVS2-745 b-globin (HBB) amplified products are indicated in untreated and treated specimens at the 50 mM and 100 mM doses. (B) Quatitative PCR analyses of correctly spliced WT HBB mRNA. Values in y-axes indicate HBB expression normalized to the house- keeping glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene expression and red-cell specific glycophorin A gene expression. (C) Percentage of hemoglobin A (HbA) in scramble-treated control (S) and 2'-MOE-SSO treated specimens (91-92-93) at same dose (n=3). All statistical comparisons (ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis) are test- ed against scramble control. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001.
Figure 6. 2'-MOE-SSO 91 restores the balance between α- and b-glo- bin chains ratio. Single chain analysis of α-chains to b-like chains (b, γ, d) ratio. All statistical analyses (ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis) are tested against scramble con- trol; n=3. ns=not significant, **P<0.01, ****P< 0.0001.
haematologica | 2021; 106(5)
1439