Page 220 - 2021_05-Haematologica-web
P. 220
A. Dong et al.
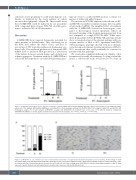
cells had a lower propensity to sickle under hypoxic con- ditions, as indicated by the lower number of yellow arrows in the right panel of Figure 8B. These results show that 2'-MOE-SSO could be indicated for use in patients with compound heterozygous IVS2-745 /b-sickle geno- type to reduce red blood cell deformities.
Discussion
2'-MOE-SSO show targeted therapeutic potential for splice mutants of b-thalassemia. They effectively act at the RNA level where the defect occurs, and lead to restoration of WT b-globin synthesis in thalassemic ery- throid cells. The increased production of functional HBB mRNA leads to increased HbA production, a restoration of the balance between α and b chains, and a reduction in α-heme aggregates. Treatment with the 2'-MOE-SSO in a cell model that reproduces a b-sickle/b-thalassemia geno-
type also leads to a sufficient HbA increase to reduce for- mation of sickle cells under hypoxia.
The increase in WT HBB expression first shown via RT- and Q-PCR was further confirmed using a direct quantifi- cation method ddPCR. The amplified effect of treatment with the 2'-MOE-SSO observed in homozygous, com- pared to heterozygous treated specimens, reflects an increased targeting of the aberrant spicing generated from two compared to a single IVS2-745 allele. While speci- mens from patient with an b0/IVS2-745 genotype already show a strong reduction of the aberrant splicing, with con- sequent increase of HbA to 60%, specimens with IVS2- 745 homozygous genotype showed even more dramatic correction upon treatment, showing an increase of HbA to 80%, an amount that could potentially be curative for patients with this genotype.
We observed no significant difference in viability or dif- ferentiation for nearly all treatments. Looking toward the future, a side-by-side study would need to be done on
AB
Figure 7. 2'-MOE-SSO 91 greatly increases amounts of wild-type b-globin mRNA. In these droplet digital polymerase chain reaction analyses, y-axes indicate relative expression of the wild-type (WT) b-globin (HBB) gene normalized to the housekeeping b-actin gene in (A) IVS2-745/b0 heterozygous sample, P4, and (B) IVS2-745 homozygous sample, P5. In both samples, 2'-MOE-SSO scramble and 2'-MOE-SSO 91 treatment were at the dose of 50 mM. All statistical comparisons (ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis) are tested against scramble-treated and non-treated sample; n=3. *P<0.1, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
Figure 8. 2'-MOE-SSO 91 can rebalance the ratio of hemoglobins and produce enough functional adult hemoglobin to prevent sickling. (A) Percentage of adult hemoglobin (HbA), sickle Hb (HbS) and fetal Hb (HbF) chains detected by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography analysis in control-untreated, scram- ble-treated and oligo 91-treated specimens, at same dose of 50 mM, n=3. (B) In vitro sickling assay. IVS2-745/b-S cells were treated with scramble or oligo 91, then exposed to hypoxia. Barbed cells with long polymers of pointy sickle chains are indicated by yellow arrows.
AB
1440
haematologica | 2021; 106(5)