Page 226 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 226
E. Karampini et al.
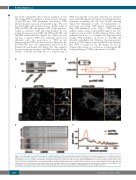
ing in the endothelial early secretory pathway. A key step during VWF biosynthesis is the proteolytic cleavage of proVWF into VWF propeptide and mature VWF, which takes place upon its arrival in the Golgi.38 We used the intracellular ratio between the two distinct forms of VWF, proVWF (ER) and mature VWF (Golgi and post- Golgi), as a measure of ER and Golgi transport by esti- mating the amount of proVWF and VWF in shCTRL and shSec22b endothelial cells (Figure 3A). While the total amount of mature VWF was markedly reduced in shSec22b cells, the proportion of VWF in the unprocessed proVWF form was increased. Therefore, the proVWF:VWF ratio was significantly increased in the Sec22b KD endothelial cells (Figure 3B). This suggests that proteolytic processing of proVWF is reduced in the absence of Sec22b, possibly due to a reduced flux of
AB
C
VWF from the ER. Consistent with this we observed increased VWF immunoreactivity in reticular perinuclear structures resembling the ER after Sec22b silencing (Figure 3C). Simultaneous with - but independent of - proteolytic processing, VWF dimers oligomerize into long VWF multimers in the Golgi.10,38 VWF multimer analysis using sodium dodecylsulfate-agarose gel elec- trophoresis showed that Sec22b silencing did not affect multimerization per se, as evidenced by high molecular weight VWF multimers in lysates of shCTRL and shSec22b endothelial cells. However, the increased pro- portion of VWF dimers in the Sec22b KD cells indicates that VWF is retained in the ER (Figure 3D and E). Together this points to a reduction of anterograde ER- Golgi trafficking of VWF in the absence of Sec22b.
DE
Figure 3. Sec22b depletion results in retention of von Willebrand factor in the endoplasmic reticulum. (A) Western blot analysis of monomeric von Willebrand factor (VWF) under reducing conditions in control and Sec22b knockdown (KD) endothelial cells (EC). Uncleaved (proVWF) and cleaved (VWF) forms are indicated by arrows. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. Molecular weight standards are indicated on the left (kDa). (B) ProVWF:VWF ratio in control and shSec22b EC (n=8, paired t-test, *P<0.05). (C) Immunofluorescent staining of VWF in shCTRL and shSec22b human umbilical vein EC (boxed areas are shown magnified on the right, size bar corresponds to 10 mm for images or 5 mm for boxed areas). (D) VWF multimer blot (4 samples from 2 independent experiments) in control and Sec22b KD EC. (E) Line graph of the densitometry of VWF multimer bands. LMWM: low molecular weight multimers; HMWM: high molecular weight multimers
1142
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)