Page 206 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 206
J. Garcia-Reyero et al.
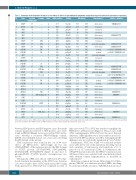
Table 1. Summary of the mutations found in 18 out 30 cases (60%) of plasmablastic lymphoma analyzed by targeted exonic next-generation sequencing.
ID
4
4 11 11 11 11 14 14 17 17 28 7 7 8 8 2 2 5 10 10 26 27 3 3 3 15 18 18 9 1 1 1 1
13
Gene
Location chromosome
Domain
---
--- --- --- --- --- SH2 SH2 SH2 PR PR --- --- --- Ac SH2 EGF-like SH2 Pro-rich ---
PR
PR
---
---
TIR
ATP binding site ---
---
PEST
---
--- STKc_Raf ---
---
Allele cDNA position
STAT3 17 EP300 22 MYC 8 MYC 8 MYC 8 MYC 8 STAT3 17 STAT3 17 STAT3 17
PRDM1 6 PRDM1 6 MYC 8
CD79B 17 SMARCA4 19 PRDM1 6 STAT3 17
NOTCH1 9 STAT3 17 PRDM1 6 CD79A 19
PRDM1 6 PRDM1 6 ARID1A 1 ARID1A 1 MYD88 3
BRAF 7 SGK1 6 SGK1 6
NOTCH2 1 MYC 8 EP300 22 BRAF 7 SGK1 6
TP53 17
Codons
Gac/Tac
A 7249
G 578
A 775
C 899
G 945
A 2255
A 2232
G 2165
G 843
G 843
T 1085
T 175
A 3295
A 2546
A 2253
A 1278
A 2232
A 1295
A 413
G 843
G 843
A 762
C 6526
C 794
G 1467
A 1950
A 1737
A 7418
T 747 agC/agT
AA change
566 D/Y
2010 M/I 23 T/S 89 Y/N 130 F/S 145 I/M 648 M/L 640 Y/F 618 G/R 203 D/E 203 D/E 192 Y/F 34 D/N
1005 R/Q 771 G/D 647 N/I 401 P/L 640 Y/F 354 S/N 76 W/* 203 D/E 203 D/E 131 G/R
2052 C/S
265 L/P
469 G/A
451 S/F
380 A/V
2400 R/*
79 S/
1731 R/H
600 V/E
136 K/*
273 R/H
Consequence* Existing_variation
deleterious COSM220689
tolerated --- tolerated --- tolerated ---
deleterious COSM4171775 deleterious ---
A 2009
atG/atA aCc/aGc Tac/Aac tTc/tCc atC/atG Atg/Ttg tAc/tTc Ggc/Cgc gaC/gaG gaC/gaG tAc/tTc Gac/Aac cGa/cAa gGc/gAc aAc/aTc cCc/cTc tAc/tTc aGc/aAc tgG/tgA gaC/gaG gaC/gaG Ggg/Agg tGc/tCc cTg/cCg gGa/gCa tCc/tTc gCt/gTt Cga/Tga
tolerated probably damaging deleterious neutral neutral probably damaging tolerated deleterious tolerated deleterious deleterious probably damaging tolerated
--- neutral neutral deleterious deleterious deleterious deleterious deleterious tolerated deleterious
--- deleterious deleterious deleterious possibly damaging
--- COSM1155743 COSM1166777 rs811925*, COSM4160094 rs811925*, COSM4160094 ---
---
---
--- COSM1155744 COSM4745915 COSM1155743 rs143040512,COSM4406870 COSM5493940 rs811925*, COSM4160094 rs811925*, COSM4160094 ---
--- COSM85940 COSM460
---
--- COSM36210
---
---
COSM476
--- COSM10660
A 6411 T 1860 A 1004 T 1008
cGc/cAc gTg/gAg Aag/Tag cGt/cAt
Gene name,exonic location,cDNA position,single nucleotide change observed,and amino acid change predicted,together with consequences predicted using three different algorithms are shown. In addition, the dbSNP and the COSMIC identity is provided when available. ID: identity; AA: amino acid.
between EBV-positive and EBV-negative cases. Recurrent somatic mutations restricted to EBV-positive cases were found in PRDM1/Blimp1 in six cases and in STAT3 in five cases. Notably, a recurrent PRDM1/Blimp1 variant, D203E, was identified in four out of six cases, involving the PR domain of the protein.
STAT3 mutations were found in five out of 30 cases (16%), all EBV-positive. Interestingly all but one (STAT3pD566Y) of the mutations involve the SH2 domain of STAT3 protein (STAT3pY640F, STAT3pM648L, STAT3pG618R, STAT3pN647I) (Figure 2) and lead to phosphoSTAT3 (Tyr705) protein overexpression (see below).
The majority of PBL cases (16 out of 23 tested, 69%) har- bored structural abnormalities at the MYC locus. Fourteen cases were found to have a MYC translocation (60%) using break apart probes. MYC-IGH was confirmed in seven of
nine cases tested (77%). MYC was found to be amplified by FISH in two additional cases (Figure 1). Thus, in cases with MYC rearrangements, MYC-IGH was the most frequent alteration. Although there was a clear trend for an associa- tion between EBV positivity and MYC rearrangement the difference was not statistically significant (c2 test, P=0.06).
Furthermore, MYC was found to be mutated in three cases with all but one of the mutations involving exon 2 and consisting of transversions and transitions at C: G pairs (4 out of 7 mutations) (Table 1). Furthermore, the MYCp79S mutation involves the WRCY consensus motif. All these features are consistent with a mechanism related with aberrant somatic hypermutation, as described in early reports.16
Mutations common mutations diffuse large B-cell lym- phoma (DLBCL), not otherwise specified (NOS), involving B-cell receptor (BCR) activation, TLR/NFκB, histone-mod-
1122
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)