Page 94 - 2021_02-Haematologica-web
P. 94
C. Lagresle-Peyrou et al.
A
B
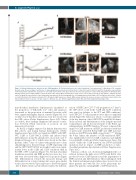
Figure 2. Patient fibroblasts are affected by the G12R mutation. (A) Proliferation kinetics for control fibroblasts (Ctrl) and patient 3’s fibroblasts (P3), using the Incucyte assay. The percentage of confluence (%, upper graph) was measured every 6 hours (h) for 6 days (n=3 wells for both Ctrl and P3). The graph is representative of two independent experiments. Evaluation of cell death (represented as the green fluorescent cells, lower panel) for control (Ctrl) and patient 3’s fibroblasts (P3), with the Cytotox green reagent added 6 h after the start of the culture. Measurements were made every 6 h for 6 days (n=3 wells for Ctrl and P3), using the Incucyte assay. The graph is representative of two independent experiments. (B) Holotomographic live cell imaging was performed with a 3D Cell Explorer microscope. Cultures of control fibroblasts (left panels) and patient 3’s fibroblasts (right panels) are shown. White arrows indicate the nuclear envelope, and brown arrows indicate the mitochondrial network. Scale bar =10 mm, 1 pixel= 0.188 mm. See also Online Supplementary Video M1 and Online Supplementary Figure S2A.
mitochondrial membrane depolarization (quantified as the proportion of “DILC1(5) low” cells) and apoptosis (measured as the proportion of annexin-V-positive cells) were significantly higher than in controls (Figure 3B). It is worthy of note that these alterations were not observed in the GFP- subset (Online Supplementary Figure S1D). Taken as a whole, these findings emphasize the specific correla- tion between RAC2 mutations at position 12 and impaired cell survival.
As RAC2 is highly expressed in human hematopoietic BM subsets and during human thymopoiesis (Online Supplementary Figure S1E), we transduced HSPC with WPI, WT, G12R or G12V RAC2 cDNAs and induced their differentiation along the granulocyte, monocyte and T- lymphoid lineages, all of which were absent in the three patients. After 7 days of culture with granulocyte colony stimulating factor, the percentage of GFP-expressing cells and the GFP+CD15+CD11b+ neutrophil counts were signif- icantly lower in the G12R and G12V conditions than in the WPI or WT conditions (Figure 3C). The mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS production were also low, and were associated with a high level of apoptosis (Figure 3D). Differentiation towards the monocyte lineage and differentiation in colony-forming unit assays gave similar results (data not shown). Upon exposure to the Notch ligand
-like-4 (DL4) culture system (which enables the differen-
tiation of HSPC into CD7+ T-cell progenitors in 7 days24), the GFP+ subset count in the G12R and G12V conditions was very low (relative to the WT and WPI conditions), and GFP+CD7+ T-cell progenitors were almost completely absent (Figure 3E). Taken as a whole, our results underline: (i) the key function of the GDP/GTP-bound RAC2 balance in the survival and differentiation of the lympho-myeloid compartment; and (ii) the involvement of the RAC2 sig- naling pathway in HSPC function. We next compared the impact of G12R mutation on HSPC proliferation with that of previously described RAC2 LOF and GOF missense mutations (p.D57N and p.E62K, respectively).15,16,19 During the 8-day culture, the number of GFP+-transduced HSPC was significantly lower in G12R conditions and slightly lower in E62K conditions (Online Supplementary Figure S3A and B). Unlike the G12R mutation, the D57N and E62K mutations had no impact on ROS production or mito- chondrial membrane depolarization (Online Supplementary Figure S3C).
Taken as a whole, our observations highlighted the cor- relation between the high active GTP-bound RAC2 state produced by the G12R mutation and the impairment of HSPC survival and differentiation. These findings fit with the clinical and immunological phenotype observed in our three patients and with the less severe phenotype dis- played by patients carrying E62K or D57N mutations.
408
haematologica | 2021; 106(2)