Page 53 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 53
SNS driven hypertension enhances hematopoiesis
the proximal aorta and aortic arch. We observed increases in plaque size between the groups (Figure 1D, E), suggest- ing that sympathetically driven hypertension may pro- mote accelerated plaque growth. We further explored the lesion characteristics and noted a significant increase in the abundance of lipid within the lesions from the BPH/Apoe-/- mice (Figure 1F). A significant increase in plaque macrophages were accompanied by a decrease in plaque collagen in the BPH/Apoe-/- mice (Figure 1G, H), suggesting that chronic sympathetic activation was pro- moting remodeling of lesions in an adverse, unstable man-
ner. This plaque phenotype in the BPH/Apoe-/- mice res- onates with the findings of Dutta et al. in the context of acute SNS stimulation during a MI.21
Hypertensive Apoe–/– mice do not develop endothelial dysfunction
Endothelial dysfunction is a generally accepted conse- quence of hypertension.27 To determine if the enhanced atherogenesis in BPH/Apoe-/- mice was the result of endothelial dysfunction we assessed the vascular respons- es in aortas from the BPH/Apoe-/- mice in comparison with
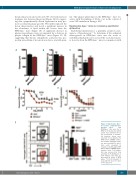
ABC
D
E
F
Figure 2. Hypertensive Apoe-/- do not have endothelial dys-
function. Apoe-/-
and BPH/Apoe-/- mice were fed a WTD for 16 weeks after which aortas were harvested for ex vivo assessment of endothe- lial function. Aortas were assessed for A) diameter, B) KPSS and C) L-NAME contrac- tion. Further myograph analy- ses were preformed to deter- mine aortic relaxation in response to D) ACh and E) SNP with or without L-NAME admin- istration. Aortic T-cell infiltra- tion was assessed by flow cytometry for F) Abundance of CD4+ T-helper cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM where **P<0.01 (Student’s t- test). A,B) n=6-10,C) n= 6-8, D)
n= 4-6, E,F) n=6.
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)
459