Page 220 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 220
C.S. Link-Rachner et al.
AB
C
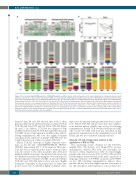
Figure 2. T-cell receptor alpha (TRα) repertoire of SIB-noATG patients and their donors. (A) Read frequencies (%) representing shared clonotypes between patient and donor repertoires on day 60 (left) and day 180 (right) are shown. Darker shading indicates higher read frequencies. (B) Simpson’s diversity index (Ds) of the naïve and memory TRα repertoires for patients and their donors (D). TRα diversity on day 60 post transplantation (d60) and day 180 (d180) post transplantation for the patients TCR_002, TCR_011, TCR_024, TCR_040 and TCR_063 are plotted. (C) Distribution of TRα clonotypes in the CD8+ naïve (upper panels) and memory (lower panels) repertoires of each patient and donor. Starting on the left, the first bar represents the donor's repertoire (Don), followed by the patient's repertoire on day 60 post transplantation (60) and day 180 post transplantation (180). Frequent clonotypes (frequency of >1% of TRα reads) are shown in color. Each pair of donor and recipient identical clonotypes is shown in the same color (separately for the naïve and memory repertoires). All clonotypes with a TRα read frequency between 0.1 and 1.0% are in white; frequencies less than 0.1% are in gray. PN: patient’s naïve repertoire; PM: patient’s memory repertoire; DN: donor’s naïve reper- toire; DM: donor’s memory repertoire; n.a.: not available.
between days 60 and 180 showed that both of these patients suffered from CMV reactivation on days 93-100 in TCR_024 and days 10-59 and day 152 in TCR_040 (Figure 2B and C). In addition, TCR_024 was diagnosed with aGvHD Grade II on day 88. TCR_040 suffered from Grade I aGvHD on day 74 and extensive cGvHD on day 136 fol- lowing transplantation. Of note, the highly dominant clonotypes in the repertoire of patient TCR_040 were not found in the donor, in contrast to patient TCR_024.
Patient TCR_011 developed a highly dominant clono- type on day 60 (AA: CATDAPPSNDYKLSF; TRAV17, TRAJ20), representing 40.1% of the memory TRα reper- toire that was not present in the donor’s memory reper- toire. In contrast to the other 2 patients who developed highly dominant clonotypes, this patient did not have any documented viral infections during the observation period but did experience extensive cGvHD on day 142. Patients TCR_063 and TCR_002 did not show any new "highly dominant" clonotypes in their repertoires at either time point because the documented highly dominant clono-
types were already frequently present in the donor’s reper- toire. Patient TCR_063 did not have any viral complica- tions and had limited cGvHD only on day 93 following transplantation. Patient TCR_002 first developed aGvHD only on day 93; CMV viral load was detectable in this patient but remained below the quantifiable level of 300 IU/mL and was not considered clinically relevant.
Diversity of T-cell receptor-α in relation to the application of ATG or PTCy
The sequencing results obtained for the UD-ATG, mmUD-ATG, UD-noATG and Haplo-PTCy groups, including the obtained TRα reads and clonotypes, are shown in Online Supplementary Table S2. Interestingly, patients who did not receive ATG or PTCy (UD-noATG) had the highest mean diversity in the naïve repertoire of all groups, with a Ds of 0.998761 on day 60 and 0.999677 on day 180 following transplantation. Indeed, these patients did not show any highly frequent clonotypes at all, and clonotypes with frequencies of more than 1.0%
626
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)