Page 57 - Haematologica-5
P. 57
Renal accumulation of MSP1 in sickle cell disease
F-actin. RON kinase inhibitor (RONi, BMS-777607) signif- icantly reduced RON signaling. Moreover, injections of RONi in young SCD mice prevented the development of glomerular disease, substantially reducing glomerular hypertrophy, capillary dilation and congestion, and endothelial injury.
Taken together, these data demonstrated that renal glomerular accumulation of MSP1 and the activation of RON kinase were involved in the induction of renal endothelial injury in SCD mice. Inhibition of RON kinase activation is a novel approach to prevent CKD develop- ment in SCD.
A
B
C
D
E P=5x10-16 F P=8x10-9
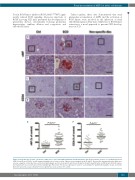
Figure 2. Renal disease in sickle cell disease (SCD) mice is associated with significant endothelial injury. (A-D) Representative pictures of von Willebrand factor (vWF) (A and B) and CD34 (C and D) immunostaining (red) of renal sections. Squares show enlarged areas (B and D). Non-specific primary antibodies (Abs) were used as a negative control. Bar sizes on the microphotographs are 100 μm (A and C) and 40 μm. (B and D). (E and F) Quantification of vWF (E) and CD34 (F) expres- sion in glomeruli cross sections is performed using ImageJ Fiji version. Five mice per group were used for each staining. For quantification graphs, means are shown. Each dot represents a value obtained from one glomerulus cross-section. Ctrl: control.
haematologica | 2018; 103(5)
789