Page 79 - Haematologica-April 2018
P. 79
Gfi1b in AML and MDS
AB
CDH
EF
G
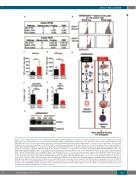
Figure 7. Loss of Gfi1b deregulates acute myeloid leukemia (AML) signaling pathway. (A) Analysis to see which pathways were enriched in GFI1B low-expressing blast cells in two independent sets of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or AML patients compared to the expression pattern found in GFI1B high-expressing MDS/AML blast cells. The same approach was repeated for Gfi1b-expressing and Gfi1b-non-expressing leukemic cells from our mice experiments. As an overlap, enrichment was observed in pathways of JAK-STAT-, MAPK- and ROS-related signaling. (B) Representative flow cytometric analysis of bone marrow (BM) from Gfi1bfl/flMxCretgNUP98/HOXD13tg mice compared to Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98/HOXD13tg mice showing the gating strategy for determining ROS low and ROS high levels. (C) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for ROS in the ROS-low population of c-Kit+ blast cells derived from Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98/HOXD13tg (n=6) and Gfi1bfl/flMxCretgNUP98-HOXD13tg (n=5); *P=0.0488. (D) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for ROS in the ROS-high population of c-Kit+ blast cells derived from Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98-HOXD13tg (n=6) and Gfi1bfl/flMxCretg NUP98/HOXD13tg (n=5); *P=0.0191. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of p38 MAPK (pT180/pY182) in CD117+ blast cells derived from Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98/HOXD13tg (n=5) and Gfi1bfl/flMxCretg NUP98/HOXD13tg (n=6); *P=0.0144. (F) Flow cytometric analysis of Akt (pS473) in c-Kit+ blast cells derived from Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98/HOXD13tg (n=4) and Gfi1bfl/flMxCretg NUP98/HOXD13tg (n=5); **P=0.0040. (G) FoXO3 protein level was detect- ed in nuclear extraction (NER)- and cytoplasmic extraction (CER)-derived BM cells from Gfi1bfl/flMxCretgNUP98/HOXD13tg and Gfi1bfl/flMxCrewtNUP98/HOXD13tg. (H) Working model hypothesis: normal levels of Gfi1b lead to reduced ROS levels, resulting in normal maturation and differentiation of progenitor cells. Loss of Gfi1b in leukemic cells is associated with higher ROS levels, which have been shown to promote AML development. However, through a still undefined mechanism, this results in lower levels of p38 MAPK and pAkt and higher levels of unphosphorylated FoXO3, which might explain the increased number of functional leukemic stem cells in the Gfi1b-deficient AML population. LSC: leukemic stem cells.
haematologica | 2018; 103(4)
623