Page 87 - 2020_08-Haematologica-web
P. 87
Resolving mediators are altered in multiple sclerosis
A
B
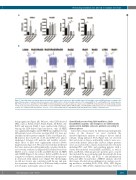
Figure 5. Specialized pro-resolving mediators biosynthetic enzymes and receptors are differentially expressed in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients according to the clinical disease phase. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC, 2x106 cells) from healthy subjects (n=5), relapsing MS (n=7), remitting MS (n=5), and progressive MS (n=5) patients were quantified for their mRNA content by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of lipid mediator biosynthesizing enzymes COX-2, 5-LOX, 12-LOX and 15-LOX (A) and of SPMs receptors ALX/FPR2, GPR32/DRV1, GPR18/DRV2, ChemR23/ERV and BLT1 (B). Data are means±standard error of mean of 5-7 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test.
being significant (Figure 2B). Of note, other DHA-derived SPM, such as RvD2, RvD3, RvD4 RvD6, AT-RvD1, AT- RvD3 and maresin (MaR) 1 were undetectable (Table 2). Among the EPA-derived lipid mediators, only 12-HEPE was significantly higher and 18-HEPE was slightly lower in MS patients; levels of E-series resolvins (RvE 1-3) were not identified in these patient samples (Table 2 and Figure 2C). Of interest, the total levels of AA and DHA were almost unchanged between MS patients and healthy subjects, while those of EPA were significantly reduced (Online Supplementary Figure S1). We next observed that all the LM that were increased in MS significantly correlated with dis- ease severity, evaluated as Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores, except for LTB4 and EPA-derived 12-HEPE and 5-HEPE (Figure 3). In contrast, RvD1 and PD1 showed a negative correlation, inasmuch as their levels progressive- ly decreased with clinical score (Figure 3B). Interestingly, we did not observe any correlation with the age and gen- der of patients, whereby levels of SPM were fairly constant in both males and females (data not shown).
Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators, their biosynthetic enzymes and receptors are differentially expressed in multiple sclerosis patients according to disease phase
Since MS is characterized by different and independent forms of the disease,1-3 we next stratified the metabololipidomics analysis according to disease clinical subtype. Using unbiased PCA (Figure 4A), we observed that each form of disease and healthy subjects were asso- ciated with distinct LM profiles. Indeed, relapse patients were associated with a cluster characterized by few LM, including PD1 and TXB2 and remitting patients with a cluster that included several HEPE and HETE, as well as LTB4 and RvD1, while progressive patients gave a cluster that included the most abundant and diversified LM, from pro-inflammatory PGE2 and PGD2 to anti-inflammatory LXA4 and LXB4. In particular, ANOVA analysis showed that many AA-derived pro-inflammatory and pro-resolv- ing mediators, including PGD2, PGE2, LXA4, LXB4 (Figure 4B) as well as TXB2 (Online Supplementary Figure S2A) fol-
haematologica | 2020; 105(8)
2063