Page 179 - 2020_08-Haematologica-web
P. 179
Apoptosis induced by selective BH3-mimetics
ABC
DEF
G
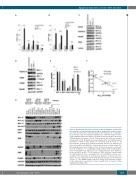
Figure 2. BH3-profiling and genetic silencing of BCL-XL and MCL-1 confirms that these proteins are important therapeutic targets independent of protein expres- sion. (A-D) The importance of the anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-XL (A, C) and MCL-1 (B, D) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was confirmed using short inter- fering (si)RNA-mediated knockdown. (A) Apoptosis was investigated 48 h after siRNA-mediated knockdown of BCL-XL. Data shown are the mean and standard deviation (SD) (n=3). (B) Apoptosis was investigated 24 h after siRNA-mediated knockdown of MCL-1. Data shown are the mean and SD (n=3). (C, D) Representative western blots showing knockdown efficiency are displayed for BCL-XL (C) and MCL-1 (D). GAPDH or a-tubulin was used as a loading control. (E,F) BH3-profiling was performed using selected cell lines and exposure of permeabi- lized cells to BIM (10, 1 or 0.1 mM), BAD (10 mM) or XXa1_Y4eK (10 mM) peptides before staining with JC-1 and fluorescence reading over time. Data shown are the mean and SD (n=4-5). (F) The response to XXa1_Y4eK was correlated with the half maximal effective concentration (EC50) for A1331852. Cell lines corre- sponding to the data points are indicated. (G) Expression of BCL-2 proteins in DLBCL cells was analyzed by western blotting. As this was done on two independ- ent gels (*, #) two GAPDH loading controls are shown. A representative example of five independent experiments is shown. Quantification is shown in Online Supplementary Figure S2A.
haematologica | 2020; 105(8)
2155