Page 74 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 74
X. Fan et al.
P<0.05) in both young and aged monkeys. Correlations were also high with B cells, known to be produced from HSPC locally in the BM, but clonal contributions to T cells were very distinct and poorly correlated, given that the final stages of T-cell development occur primarily in the thymus, thus T cells in the BM have returned back from the blood and represent the total body clonal T-cell land- scape.23 Figure 2D groups clonal contributions by degree of lineage bias for the young and aged macaques and demon- strates no appreciable contributions from HSPC clones
contributing solely or in a highly biased way to NRBC but not to other hematopoietic lineages. The bias and relative size of barcoded clones in other lineages are shown in Online Supplementary Figure S2.
Erythroid and myeloid colony-forming units share clonal contributions
Colony-forming unit assays are widely used to study HSPC output and differentiation at a single cell level. Previous publications reported erythroid-biased output
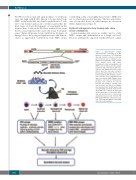
Figure 1. Experimental design.
Oligonucleotides consisting of a 6bp library ID followed by a 27-35bp high diversity random sequence barcode were inserted into a lentiviral vector flanked by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer sites. RM CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) were mobilized into the periph- eral blood (PB), collected by apheresis, enriched via immunoselection, trans- duced with the barcoded lentiviral library, and infused back into the total body irradiation (TBI) irradiated autolo- gous macaque. After engraftment, PB and bone marrow (BM) samples were obtained, and various hematopoietic lineages were purified for barcode retrieval and analyses. Lineage cells and nucleated red blood cell (NRBC) were purified from the BM and/or PB. Colony-forming unit (CFU) derived from CD34+ BM cells cultured in semi-solid media, and mature red blood cell (RBC) and reticulocytes were enriched via depleting nucleated cells from the PB. DNA and/or RNA were extracted for bar- code PCR, high-throughput sequencing, and custom data analysis.
vs. versus
1816
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)