Page 261 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 261
DNM2 is required for GPVI signaling
against membrane raft disruption and indicate that DNM2 plays a proximal role in GPVI signaling.
The positive role of DNM2 in GPVI signaling contrasts with its commonly reported function in attenuating recep- tor signaling. Lack of DNM2-dependent RME enhances responses to thrombopoietin in platelets and MK and to epidermal growth factor and interleukins 5 and 7 in other cells.9-12 Dynasore treatment also inhibits the desensitiza-
AB
tion of the purinergic receptors P2Y1 and P2Y12 in human platelets.13 Thus, DNM2 differentially regulates signaling depending on the receptor it is linked to. The GPVI-asso- ciated FcR γ-chain contains two putative endocytic YxxL motifs that are present within its immunoreceptor tyro- sine-based activation motif. Whether these motifs recruit the endocytic machinery necessary to down-regulate GPVI is unclear, as their mutation in mouse platelets abol-
C
D
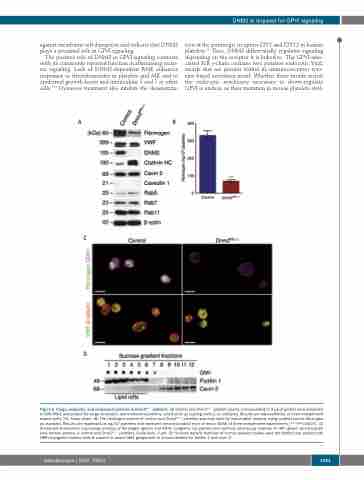
Figure 6. Cargo, endocytic, and endosomal proteins in Dnm2Plt–/– platelets. (A) Control and Dnm2Plt–/– platelet lysates corresponding to 2 mg of protein were subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed for cargo, endocytic, and endosomal proteins, and β-actin as loading control, as indicated. Results are representative of three independent experiments. HC: heavy chain. (B) The fibrinogen content of control and Dnm2Plt–/– platelets was evaluated by immunoblot analysis using purified mouse fibrinogen as standard. Results are expressed as ng/106 platelets and represent mean±standard error of mean (SEM) of three independent experiments (***P=0.0007). (C) Structured illumination microscopy analysis of fibrinogen (green) and CD41 (magenta; top panels) and confocal microscopy analysis of vWF (green) and β-tubulin (red; bottom panels) in control and Dnm2Plt–/– platelets. Scale bars, 3 mm. (D) Sucrose density fractions of human platelet lysates were dot-blotted and probed with HRP-conjugated cholera toxin B subunit to detect GM1 ganglioside or immunoblotted for flotillin 1 and cavin 2.
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1421