Page 259 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 259
DNM2 is required for GPVI signaling
derived fibrinogen.31,32 To evaluate the contribution of DNM2-dependent RME in the process, the fibrinogen content of Dnm2Plt–/– platelets was compared to that of vWF, which is synthesized by MK and is also stored in platelet α-granules (Figure 6A).33 Immunoblot analysis showed severe fibrinogen reduction in Dnm2Plt–/– platelet lysates, but normal expression of vWF. Quantification of the immunoblots using purified mouse fibrinogen as stan- dard revealed that 106 Dnm2Plt–/– platelets contained 71±6 ng fibrinogen, compared to 333±27 ng in 106 control platelets (n=3 in each group) (P=0.0007), a 79% decrease (Figure 6B).
The fibrinogen content of control and Dnm2Plt–/–platelets was further evaluated by structured illumination microscopy and compared to that of the αIIb subunit (CD41) of its receptor, the integrin αIIbβ3 (Figure 6C, top panels). In control platelets fibrinogen was observed in large puncta, consistent with its presence in α-granules.33 By contrast, Dnm2Plt–/– platelets had severely reduced fib- rinogen content, with about 90% of Dnm2Plt–/– platelets presenting barely detectable fibrinogen positive α-gran- ules. CD41 resided on the platelet surface and in small vesicles or granules within platelets, independent of DNM2 expression, consistent with the association of the integrin αIIbβ3 with multiple intracellular platelet com- partments that include α-granules and the open canalicu-
AB
lar system.34 By contrast, vWF was normally packaged in Dnm2Plt–/– platelets (Figure 6C, bottom panels). Taken together, the data show that integrin αIIbβ3-dependent uptake of plasma-derived fibrinogen requires DNM2- dependent RME.
Platelet endocytic and endosomal components
Thin-section electron microscopy studies have subdi- vided RME into clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocy- tosis (CME and CavME, respectively).1 CME is found in virtually all cells and requires cargo receptor binding to clathrin-associated adaptor protein 2 complexes to form clathrin-coated vesicles.35 Caveolae are invaginated lipid rafts rich in cholesterol, sphingolipids, and scaffolding pro- teins called caveolins and cavins that are found in many mammalian cell types.36 Platelet endocytic and endosomal components were investigated in the presence or absence of DNM2 (Figure 6A). Platelets contained clathrin heavy chain required for CME and its expression was increased in Dnm2Plt–/– platelets. Cavin 2 (also known as SDPR, PS- p68) was detected in platelets, but not caveolin 1, which is required for CavME. Ruling out poor antibody reactivity, a strong caveolin 1 signal was observed at the expected molecular weight of 21 kDa with mouse lung tissue lysates (data not shown).37
As an additional control and because cavin 2 associates
CD
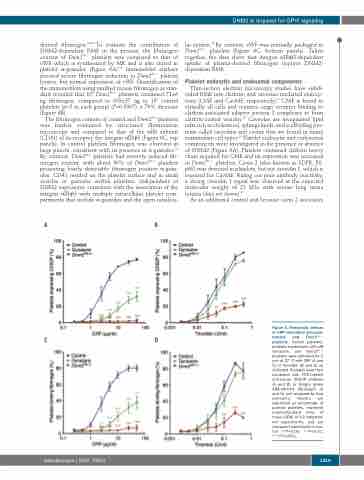
Figure 4. Hemostatic defects of CRP-stimulated dynasore- treated and Dnm2Plt–/– platelets. Control platelets, platelets treated with 100 mM dynasore, and Dnm2Plt–/– platelets were activated for 2 min at 37°C with CRP (A and C) or thrombin (B and D) as indicated. Platelets were then incubated with FITC-labeled anti-mouse CD62P antibody (A and B) or Oregon green 488-labeled fibrinogen (C and D) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are expressed as percentage of positive platelets, represent mean±standard error of mean (SEM) of 3-6 independ- ent experiments, and are compared statistically to con- trol (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001).
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1419