Page 175 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 175
Ph– ALL cytogenetics and allogeneic HCT outcomes
the sole cytogenetic abnormality with a HR≤0.6 for relapse, and was categorized as favorable risk. The remaining cytogenetic markers, including normal cytoge- netics, were categorized as intermediate risk (n=1566). This novel allogeneic HCT-specific cytogenetic risk clas- sification (hereafter called CIBMTR ALL risk) was found to be prognostic for both post-transplant relapse (Online Supplementary Figure S1) and leukemia-free survival (log- rank P=0.04) (Figure 1B). Furthermore, in the multivari- able Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for recipi- ent age, pre-transplant remission status, conditioning intensity, Karnofsky Performance Status, donor type, and GvHD prophylaxis, patients with CIBMTR adverse-risk cytogenetics had a higher risk of treatment failure (HR=1.26; 95% CI: 1.01-1.57, P=0.04), and those with favorable risk had a lower risk (HR=0.6; 95% CI: 0.35- 1.02, P=0.06) compared to those with intermediate-risk cytogenetics (Table 5). There was a significantly greater risk of treatment failure in those with adverse versus favorable risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HR=2.10; 95% CI: 1.19-3.70, P=0.01). Similarly, there was a significantly greater risk of overall mortality in patients with adverse versus favorable risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HR=1.91; 95% CI: 1.08-3.38, P=0.03).
Discussion
This large CIBMTR analysis of allogeneic HCT recipi- ents with Ph– ALL defined a cytogenetic classification spe- cific to allogeneic transplantation. Of the established
Table 3. Multivariable model of prognostic factors for post-transplant relapse.
Factors N
Conditioning regimens
MAC (+TBI) 1334 MAC (-TBI) 253 RIC/NMA 96
Remission status pre-alloHCT CR1 986 CR2 733
Cytogenetics
Complex karyotype* 51 Monosomy 7* 33
HR (95% CI)
1.0
1.54 (1.22-1.96) 1.9 (1.38-2.61)
1.0
1.71 (1.44-2.04) 1.69 (1.06-2.69)
2.11 (1.04-4.27)
P-value
<0.001 <0.001
<0.001 0.03
0.04
N: number; HR: hazard ratio; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; MAC: myeloablative con- ditioning;TBI: total body irradiation; RIC: reduced-intensity conditioning; NMA: non-mye- loablative; alloHCT: allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation; CR1: first complete remission; CR2: second complete remission. *Adjusted for monosomal karyotype.
Figure 2. Cytogenetic risks by modified Medical Research Council – Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group cytogenetic risk classification and post-transplant out- comes. All multivariable models were adjusted for recipient age, disease status, conditioning intensy, Karnofsky Performance Status, donor type and graft-versus- host disease prophylaxis. mMRC-ECOG: modified Medical Research Council-Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group classification with its three cytogenetic risk groups on Y-axis, relative to the Intermediate risk (reference with HR=1) on X-axis; LFS: leukemia-free survival; OS: overall survival.
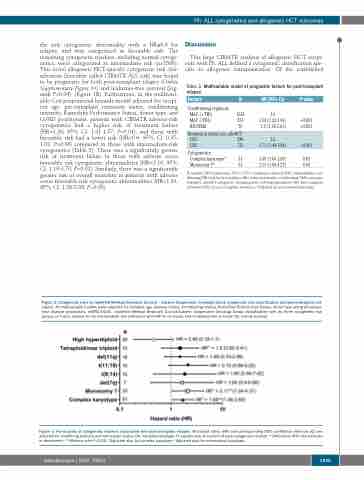
Figure 3. Forest plots of cytogenetic markers associated with post-transplant relapse. All hazard ratios (HR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) are adjusted for conditiong intensity and remisssion status; CK: complex karyotype; N: sample size of carriers of each cytogenetic marker. * Defined as 40% risk increase or decrement; **Markers with P<0.05; ΨAdjusted also for complex karyotype. DAdjusted also for monosomal karyotype.
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1335