Page 120 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 120
B.Z. Carter et al.
to limited cell numbers in some samples), CML mouse BM CD45+ cells tended to be more sensitive to the BH3 pep- tides tested, but were statistically significantly more sensi- tive than cells from control mice to the NOXA peptide (P=0.044) (Figure 3A). CML mouse BM LSK cells overall were statistically significantly more sensitive to BH3 pep- tides, especially to BIM (P=0.034) and NOXA (P=0.00052), than were controls (Figure 3B). These results indicated that CML cells, and stem/progenitor cells, were more sen- sitive to BH3 peptide-induced apoptosis than controls.
Combined activation of p53 and inhibition of BCR-ABL1 demonstrates strong anti-leukemia activity and inhibits leukemic lineage-SCA-1+C-KIT+cells in chronic myeloid leukemia mice
Bone marrow cells from Tet-off Scl-tTa-BCR-ABL1/GFP mice were injected into irradiated recipient FVB/N mice. After confirming the development of neutrophilic leuko- cytosis in PB (4 weeks after cell injection), mice were untreated, or treated with imatinib, DS-5272, or the com- bination, following the scheme shown in Figure 4A. At the
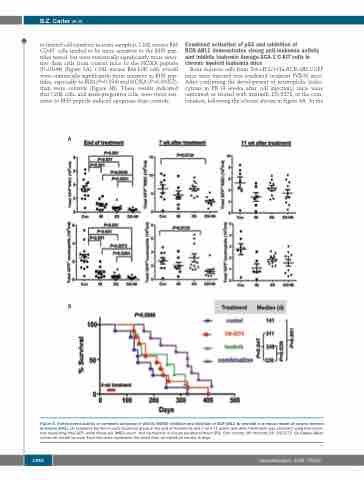
A
B
Figure 5. Anti-leukemia activity of combined activation of p53 by MDM2 inhibition and inhibition of BCR-ABL1 by imatinib in a mouse model of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). (A) Leukemia burden in each treatment group at the end of treatments and 7 and 11 weeks (wk) after treatments was assessed using flow cytom- etry measuring total GFP+ white blood cell (WBC) count and neutrophils in mouse peripheral blood (PB). Con: control; IM: imatinib; DS: DS-5272. (B) Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival. Each dot/mark represents the result from an individual mouse; d: days.
1280
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)