Page 119 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 119
MDM2 and BCR-ABL1 inhibition targets CML stem cell
increased p53 signaling in the BM of CML mice suggested that CML cells are protected from cell death, but possibly could still have a propensity for p53-mediated apoptosis. Consequently, they could be more sensitive to BH3 pep- tides than normal controls. To test this, we treated BM cells from Tet-off CML (n=6) and Tet-on control (n=5) mice with various BH3 peptides in order to assess the pool
of sequestered pro-apoptotic, BH3-only proteins (priming) in CD45+ and CD45+LSK cells. Owing to the limited num- ber of cells available in the LSK population, priming results were calculated for only those samples in which sufficient LSK cells (>10 cells) were measured (n=5 for Tet-off and n=2 for Tet-on).
Although the variations were large, (likely due, in part,
B
C
A
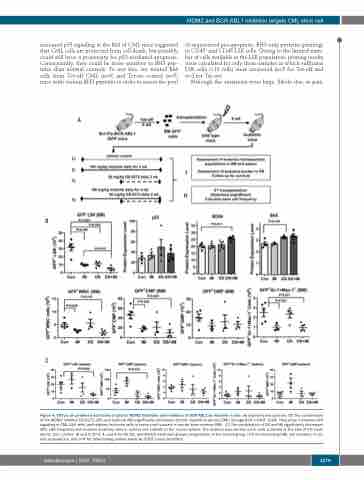
Figure 4. Effects of combined activation of p53 by MDM2 inhibition and inhibition of BCR-ABL1 by imatinib in vivo. (A) Experimental scheme. (B) The combination of the MDM2 inhibitor DS-5272 (DS) and imatinib (IM) significantly decreases chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) lineage-SCA-1+C-KIT+ (LSK) frequency, increases p53 signaling in CML LSK cells, and reduces leukemia cells in various cell subsets in mouse bone marrow (BM). (C) The combination of DS and IM significantly decreases CML LSK frequency and reduces leukemia cells in various cell subsets in the mouse spleen. The analysis was carried out in cells collected at the end of the treat- ments. Con: control. (B and C) N=3, 4, and 4 for IM, DS, and IM+DS treatment groups; respectively. In the control group, n=5 for measuring CML cell numbers in var- ious populations, and n=4 for determining protein levels by CyTOF mass cytometry.
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1279