Page 39 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 39
RUNX1 variant curation
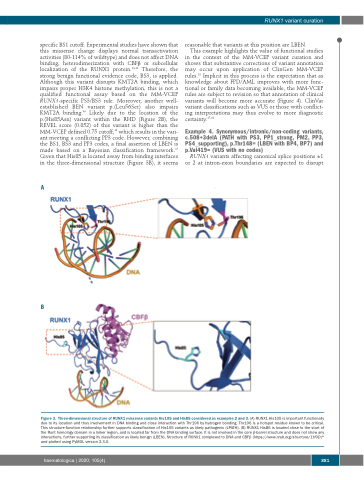
specific BS1 cutoff. Experimental studies have shown that this missense change displays normal transactivation activities (80-114% of wildtype) and does not affect DNA binding, heterodimerization with CBFβ or subcellular localization of the RUNX1 protein.44,46 Therefore, the strong benign functional evidence code, BS3, is applied. Although this variant disrupts KMT2A binding, which impairs proper H3K4 histone methylation, this is not a qualified functional assay based on the MM-VCEP RUNX1-specific PS3/BS3 rule. Moreover, another well- established BEN variant p.(Leu56Ser) also impairs KMT2A binding.46 Likely due to the location of the p.(His85Asn) variant within the RHD (Figure 2B), the REVEL score (0.852) of this variant is higher than the MM-VCEP defined 0.75 cutoff,18 which results in the vari- ant meeting a conflicting PP3 code. However, combining the BS1, BS3 and PP3 codes, a final assertion of LBEN is made based on a Bayesian classification framework.15 Given that His85 is located away from binding interfaces in the three-dimensional structure (Figure 3B), it seems
A
reasonable that variants at this position are LBEN.
This example highlights the value of functional studies in the context of the MM-VCEP variant curation and shows that substantive corrections of variant annotation may occur upon application of ClinGen MM-VCEP rules.18 Implicit in this process is the expectation that as knowledge about FPD/AML improves with more func- tional or family data becoming available, the MM-VCEP rules are subject to revision so that annotation of clinical variants will become more accurate (Figure 4). ClinVar variant classifications such as VUS or those with conflict- ing interpretations may thus evolve to more diagnostic
certainty.47,48
Example 4. Synonymous/intronic/non-coding variants, c.508+3delA (PATH with PS3, PP1_strong, PM2, PP3, PS4_supporting), p.Thr148= (LBEN with BP4, BP7) and p.Val419= (VUS with no codes)
RUNX1 variants affecting canonical splice positions ±1 or 2 at intron-exon boundaries are expected to disrupt
B
Figure 3. Three-dimensional structure of RUNX1 missense variants His105 and His85 considered as examples 2 and 3. (A) RUNX1 His105 is important functionally due to its location and thus involvement in DNA binding and close interaction with Thr196 by hydrogen bonding. Thr196 is a hotspot residue known to be critical. This structure-function relationship further supports classification of His105 variants as likely pathogenic (LPATH). (B) RUNX1 His85 is located close to the start of the Runt homology domain in a linker region, and is located far from the DNA binding surface. It is not involved in the core β-barrel structure and does not show any interactions, further supporting its classification as likely benign (LBEN). Structure of RUNX1 complexed to DNA and CBFβ (https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1H9D)82 and plotted using PyMOL version 2.3.0.
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
881