Page 98 - 2020_02-Haematologica-web
P. 98
L. Wang et al.
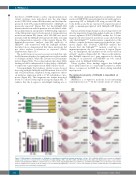
the choice of NMP cell fate, a series of point mutations in critical cysteines were introduced into the ring finger motif (C420/423A, named RM hereafter) and the zinc fin- ger motif (C14/17A, named ZM hereafter) of Irf2bp2b, as previously reported15 (Figure 5A). For the Irf2bp2b RM mutant, interaction with its partners was abolished, while the polymerization and putative DNA-binding capacities of the ZM mutant were both abrogated. A tetramerization motif from human P53 (amino acids 324-355) was fused in-frame with the Irf2bp2b ZM mutant (tet-ZM), restoring the polymerization capacity of this mutant (Figure 5A). Immunofluorescence analysis (anti-HA antibody) of HEK293T cells transfected with the Irf2bp2b mutants described above demonstrated that these mutations did not affect nuclear localization as expected (Online Supplementary Figure S7).28
The results from in vivo rescue assays revealed that only the RM mutant displayed a significant rescue effect similar to wildtype irf2bp2b, while the ZM and tet-ZM mutants did not (Figure 5B-L). These data indicate that direct DNA binding would be indispensable for the ability of Irf2bp2b to repress pu.1 gene expression in NMP cell fate choice.
Correspondingly, the luciferase activity assays showed that only wildtype Irf2bp2b and RM mutant, but not ZM and tet-ZM mutants, exhibited strong repressive effects on luciferase expression with a -1.7 kb zebrafish pu.1 pro- moter (Figure 6A). This fragment was further narrowed down to a short 132 bp region (A region) (Figure 6B). To validate that the A region is an Irf2bp2b binding site, in
vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation polymerase chain reaction (CHIP-PCR) was performed in zebrafish embryos expressing GFP or Irf2bp2b-GFP using an anti-GFP anti- body. In this assay, the pu.1 promoter A region was specif- ically co-immunoprecipitated with Irf2bp2b-GFP (Figure 6C).
Since positively charged amino acids are important to fit into the negatively charged phosphate backbone of DNA, several arginines (R10/11/36/55/59) within the C4 zinc finger motif were mutated. Luciferase assays showed that only the Irf2bp2bR55/59L double-mutant completely lost the ability to repress luciferase expression from the pu.1 pro- moter (Figure 6D). Notably, CHIP-PCR analysis has shown that the Irf2bp2bR55/59L mutant could not co- immunoprecipitate the pu.1 promoter A region (Figure 6C). As anticipated, this mutant lost the rescue effect in irf2bp2b-/- embryos (Figure 6E-J, K). These results indicate that Irf2bp2b represses pu.1 gene expression by directly binding to its promoter and R55/R59 are two critical amino acids for Irf2bp2b DNA binding.
Taken together, these findings suggest that Irf2bp2b most likely functions as a transcription repressor, rather than a co-repressor, in NMP fate choice during zebrafish myelopoiesis.
The repressive property of Irf2bp2b is dependent on SUMOylation
IRF2BP2 is a co-repressor molecule for its interacting transcription factors.14,17 In the current study, we demon-
A
L
BC
DE
FG
H
I
JK
Figure 5. DNA-binding is indispensable for Irf2bp2b in regulating neutrophil-macrophage progenitor cell fate. (A-L) Irf2bp2b mRNA rescue assays in irf2bp2b-/- embryos. (A) Structure of variant forms of Irf2bp2b, including wildtype (WT), and ZM, tet-ZM, and RM mutants. (B-L) Mpx and mfap4 probes were used in whole- mount in situ hybridization (WISH) to examine the rescue effect of injecting irf2bp2b ZM (F, G), tet-ZM (H, I), and RM mutant mRNA (J, K). (L) Error bars represent the mean ± standard error of mean of 15-30 embryos. ns: not statistically significant; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (analysis of variance followed by the least significant dif- ference post-hoc test for multiple comparisons).
332
haematologica | 2020; 105(2)