Page 100 - 2020_02-Haematologica-web
P. 100
L. Wang et al.
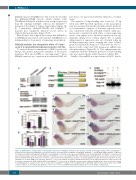
Irf2bp2b upon its SUMOylation. The results showed that the Irf2bp2b-SUMO fusion, which mimics fully SUMOylated Irf2bp2b, displayed even stronger repression than the wildtype Irf2bp2b, whereas the Irf2bp2bK496R mutant lost the ability to repress transcription (Figure 7B, E). Consistently, Irf2bp2b-SUMO and Irf2bp2bK496R mutants had completely different rescue effects in irf2bp2b-deficient mutants (Figure 7F-N).
Overall, these data support the concept that Irf2bp2b is a SUMOylated protein in cells and that SUMOylation is indispensable for its property of repressing transcription.
Irf2bp2b mediates the antagonistic effect of C/ebpα on pu.1 in neutrophil-macrophage progenitor cell fate
To ensure balanced commitment of NMP toward each lineage, the mutual antagonistic interplay of the master regulators PU.1 and C/EBPα is very important.5,41 Since Irf2bp2b represses pu.1 expression in zebrafish NMP cell
fate choice, we questioned whether irf2bp2b is a C/ebpα target.
Two putative C/ebpα binding sites located at -37 bp (CS1) and -1595 bp (CS2) upstream of the transcription start site were predicted in the zebrafish irf2bp2b promoter by bioinformatics analysis. A luciferase reporter vector was constructed with the zebrafish irf2bp2b -2.2kb pro- moter and co-transfected with either a c/ebpα-expressing vector or an empty vector. Luciferase expression was sig- nificantly enhanced by C/ebpα (Figure 8A). A similar enhancement of expression was also obtained when an mCherry-expressing vector carrying the same irf2bp2b promoter (irf2bp2b:mCherry, in a Tol2 backbone) was co- injected with c/ebpα and Tol2 transposase mRNA into zebrafish embryos (Figure 8B, C). This enhancement was completely abolished when the predicted C/ebpα binding sites were deleted in the irf2bp2b promoter (Figure 8D).
Finally, c/ebpα mRNA was injected into irf2bp2b-/- knock-
ABC
D
E
N
FG
HI
JK
LM
Figure 7. SUMOylation is indispensable for transcription repression of Irf2bp2b. (A) Western blot analysis (anti-HA) of HA-tagged wildtype (WT) and Irf2bp2bK496R mutant proteins expressed in HEK293T cells. (B) The structure of variant forms of Irf2bp2b, including WT, Irf2bp2bK496R, and Irf2bp2b-SUMO mutants. (C) Western blot analysis (anti-HA) of HA-tagged WT, Irf2bp2bK496R and Irf2bp2bE498A mutant proteins expressed in HEK293T cells. (D) HA-tagged WT or Irf2bp2bK496R mutant protein was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody from HEK293T cells co-expressing GFP-SUMO, and SUMOylated Irf2bp2b protein was detected by western blot with an anti-GFP antibody. (E) Repression of luciferase expression from the zebrafish pu.1 promoter (-1.7kb) by Irf2bp2b mutants. Error bars represent the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of at least three replicates. ***P<0.001 [analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the least significant difference (LSD) post-hoc test for multiple comparisons]. (F-M) Irf2bp2b-SUMO and irf2bp2bK496R rescue assays in irf2bp2b-/- mutant embryos. Mpx and mfap4 probes were used in whole-mount in situ hybridization to examine rescue effects of injections of irf2bp2bK496R mutant (J, K) or irf2bp2b-sumo (L, M) mRNA. (N) Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of 15-30 embryos. ns: not statistically significant; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (ANOVA followed by the LSD post-hoc test for multiple comparisons).
334
haematologica | 2020; 105(2)