Page 149 - 2020_02-Haematologica-web
P. 149
RKIP loss aggravates RAS-driven leukemogenesis
tion, only the Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip-/- genotype exhibited a full blown MPD, as evidenced by an accompanying leuko- cytosis in the peripheral blood (Figure 4C and D, and Online Supplementary Table S2).37 We then studied a poten- tial involvement of the RAS-MAPK/ERK pathway in this process. As seen in the experiments described above, Rkip deletion again enhanced the activation of ERK. Importantly, these effects on RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling were visible both in the absence of mitogens and follow- ing GM-CSF stimulation (Figure 6D and Online Supplementary Figure S6). In agreement with data from Li et al.,8 HS were detected in all Nras-mutated mice studied; however, the phenotype was mitigated in the Mx1- Cre/Nras/Rkip-/- animals. Transformation into secondary AML did not occur in any of the mice, as assessed by mor- phological and flow cytometric evaluation of peripheral blood, bone marrow and spleen (data not shown). Interestingly, although MPD development was aggravated in Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip-/- animals, the median survival was similar between Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip-/- and Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+ mice (P=0.339) (Online Supplementary Figure S7). Histopathological examination of moribund Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+ mice thereby revealed that these mice suffered from extensive HS (Online Supplementary Table S3 and Online Supplementary Figure S8). In agreement with the data from 6-month old mice, the Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip-/- mice had a mitigated HS pheno- type but an increased myeloproliferation/MPD occur- rence. Future studies, using models without the predispo- sition to HS, will, therefore, be necessary to unambigu-
ously delineate the effect of Rkip on the survival of Ras-driven MPD.
Taken together, these data indicate that RKIP aggravates the effects of mutated Nras on RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling on the one hand, as well as on myeloproliferation and MPD development on the other.
RAF kinase inhibitor protein loss is frequently observed in primary chronic myelomonocytic leukemia patient specimens and co-occurs with RAS-signaling mutations
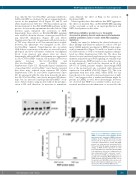
Finally, we aimed to delineate the clinical relevance of these findings and therefore analyzed a cohort of 41 pri- mary CMML patients' specimens for RKIP protein expres- sion by immunoblot (Figure 7A and B; for details of clini- cal characteristics as well as treatment regimens adminis- tered see Online Supplementary Table S4). We chose this disease because increased myelomonocytic lineage com- mitment and pathological RAS-signaling are seminal steps in its pathogenesis. RKIP protein loss was defined as pre- viously reported12,22 and could be detected in 12 of 41 (29.3%) of CMML patients' samples. Interestingly, RKIP loss at the protein level also correlated with decreased expression of its mRNA (P<0.001) (Figure 7C). This is in agreement with data from AML, where RKIP loss has been shown to be caused by increased expression of miR- 23a,21,22 and suggests that a similar mechanism might be present in CMML as well. Most interestingly, however, we observed that RKIP loss correlated with a more pro- nounced myelomonocytic phenotype, as assessed by the
A
B
C
Figure 7. Loss of RAF kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a frequent event in primary chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) patients' samples. (A) Loss of RKIP at protein level was observed in 12 of 41 (29.3%) of cases. A rep- resentative immunoblot is shown, with RKIP protein loss being present in patients 8039, 7156 and 7954. (B) Graphs showing the x-fold change in RKIP protein expression as com- pared with NB4 acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells, which were chosen as a calibrator due to their physiological RKIP expression levels.12 The expression of NB4 was arbitrarily set to 1. (C) Box plots illustrating RKIP mRNA levels in CMML patients with and without RKIP loss at the protein level. NB4 AML cells served as cal- ibrator and statistical significance was calcu- lated by the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test.
haematologica | 2020; 105(2)
383