Page 98 - 2019_12-Haematologica-web
P. 98
A.L. Young et al.
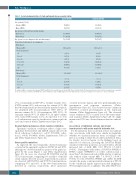
Table 1. Selected characteristics of study participants by case-control status. Cases (N=34)
Controls (N=69)
31 (44.9) 38 (55.1)
61 (48-71)
70 (62-79) 75 (53-87)
14.1 (±6.0)
6 (8.7) 2 (2.9) 4 (5.8) 18 (26.1) 31 (44.9) 8 (11.6)
6.3 (±2.8)a
0 (0.0) 6 (26.1) 13 (56.5) 4 (17.4)
Sex (cohort), N (%) Female (NHS) Male (HPFS)
Age (years) at blood draw, median (range)
Collection 1
Collection 2a
Age (years) at case diagnosis date, median (range)b Years, blood collection to case diagnosis
Collection 1, Mean (±SD)
N (%) by intervalc
<1
1 to <5
5 to <10 10 to <15 15 to <20 ≥20
Collection 2,a Mean (±SD)
N (%) by intervalc
<1
1 to <5 5 to <10 ≥10
15 (44.1) 19 (55.9)
61 (48-70)
70 (62-78) 76 (53-87)
14.2 (±6.1)
2 (5.9) 2 (5.9) 2 (5.9) 9 (26.5) 15 (44.1) 4 (11.8)
6.4 (±2.6)a
0 (0.0) 2 (16.7) 8 (66.7) 2 (16.7)
N: number; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; HPFS: Health Professionals Follow-up Study; NHS: Nurses’ Health Study; SD: standard deviation. aSecond blood samples were available for 11 cases and 21 controls in the NHS. bIn controls, defined as date of AML diagnosis for the matched case. cCase percentages do not sum to 100 due to rounding.
(7%), 12 synonymous SNV (5%), 11 splice variants (4%), 4 UTR variants (2%), and one stop loss variant (<1%). Of the 346 clonal mutations detected in the matched controls, we identified 208 non-synonymous SNV (60%), 47 intronic variants (14%), 34 synonymous SNV (10%), 30 stop gain variants (9%), 13 indels (4%), 12 splice variants (3%), and 2 UTR variants (<1%). As expected, C to T (G to A) substitutions were by far the most common in both cases and controls (Online Supplementary Figure S1C).
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction validation
Spearman correlation coefficients reflect a high corre- spondence between ECS and ddPCR variant calls at both blood collections (collection 1, r=0.97, P<0.0001; collec- tion 2, r=0.95, P<0.0001) (Online Supplementary Table S3 and Online Supplementary Figure S2).
Gene-specific mutations
As expected, the most frequently observed mutations occurred in the epigenetic regulators DNMT3A and TET2, although we observed mutations in most of the genes tar- geted by the assay (Figure 1 and Online Supplementary Figure S3). In cases, we observed 58 DNMT3A and 56 TET2 clonal variants, comprising 23% and 22% of the 252 clonal variants detected in cases, respectively. In controls, we observed 128 DNMT3A and 57 TET2 clonal mutations, comprising 37% and 16% of the 346 clonal mutations detected in controls, respectively. Most mutations
occurred in exonic regions and were predominantly non- synonymous and nonsense mutations (Online Supplementary Figure S3). The observed exonic variants in DNMT3A occurred predominantly in the functional domains (Online Supplementary Figure 4A). The observed exonic variants in TET2 occurred across the entire amino acid sequence (Online Supplementary Figure 4B). No single mutation in TET2 was observed in more than two individ- uals.
Association of individual variants and clonal hematopoiesis with acute myeloid leukemia risk
For the mutations that occurred in at least four individ- uals, associations with AML were similar in magnitude whether we classified mutation status according to the first or according to either blood collection (Table 2). Thus, for brevity, we focus herein on the findings based on either blood collection. Detecting the DNMT3A R822H variant at either time point was associated with a 14-fold increased risk of AML (OR: 14.0, 95%CI: 1.7-113.8; P=0.01). Participants with either a DNMT3A R882H or R882C variant (“R882H/C”) at either collection had a more than 7-fold increased risk of AML relative to individ- uals without either variant (OR: 7.3, 95%CI: 1.5-34.7; P=0.01). For the DNMT3A W860R and ASXL1 E1183K variants, the sparse counts prevented estimation of 95%CI by the conditional logistic regression models (implying a 95%CI range from zero to infinity). The JAK2 V617F vari-
2412
haematologica | 2019; 104(12)