Page 58 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 58
M. Mazzola et al.
ABC
DEFG
HIJ
KLMN
OPQ
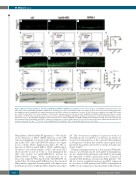
Figure 2. Myeloid cell differentiation is affected in nipblb-MO and NPMc+ mRNA injected embryos. (A-C) Confocal analyses of CD41:GFP hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) from controls, nipblb-MO and NPMc+ mRNA injected embryos at 3 days post-fertilization (dpf). The number of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-positive HSC was slightly increased in nipblb-MO, but significantly increased in NPMc+ embryos in comparison to controls. (D-G) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analy- ses on GFPlow-positive HSC. (H-J) Confocal analyses of PU.1-positive myeloid precursor cells from controls, nipblb-MO and NPMc+ mRNA injected embryos at 3 dpf. The numbers of GFP-positive myeloid precursors cells were increased in both nipblb-MO and NPMc+ embryos in comparison to controls. (K-N) FACS analyses on Pu.1 GFP-positive cells. (O-Q) Sudan black staining for mature myeloid cells in controls, nipblb-MO and NPMc+ mRNA injected embryos at 4 dpf. The mature myeloid cells were diminished in both nipblb-MO and NPMc+ embryos in comparison to controls. Images were processed as described in the Online Supplementary Methods. The scale bar represents 100 μm. ***P<0.001. ns: non-significant; MO: morpholino; CHT: caudal hematopoietic tissue; ctrl: control.
Wnt inhibitor dkk1b mRNA (50 pg/embryo).12 We validat- ed the efficiency of dkk1b mRNA injection as the GFP+ cells were diminished or absent in the hindbrain ventricle and in the CHT of the Tg(TOPdGFP) embryos in compar- ison to controls (Online Supplementary Figure S5). The co- injection of dkk1b in nipblb-MO or NPMc+ mRNA-inject- ed embryos rescued the number of GFP+ cells in the CHT (10 rescued/10 scored for both) or even diminished the GFP+ cells (n=8±3 for nipblb-MO/dkk1b; n=10±3 for NPMc+/dkk1b) (Figure 3F-H, quantification in I). Moreover, using the Wnt reporter line Tg(TOPdGFP) we verified that, following nipblb-MO injection, the canonical Wnt pathway appeared downregulated at 24 hpf but was then hyper-activated at 48 hpf (Online Supplementary Figure
S6). This observation confirmed our previous work on a zebrafish model for nipblb-loss-of-function in which we observed downregulation of the canonical Wnt pathway at 24 hpf and correlated this with the neurological defect presented by patients affected by Cornelia de Lange syn- drome (CdLS).30
Having seen hyper-activation of the canonical Wnt path- way in our zebrafish model with nipblb downregulation, we also analyzed this in humans with AML by measuring the expression of AXIN2, previously used as a reporter of canonical Wnt pathway activation in AML patients.12 We did not observe a significant increase in AXIN2 expression in our cohort of AML patients with NIPBL downregulation (NIPBL <1) in comparison to that in patients with normal or
1336
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)