Page 143 - 2019_07 resto del Mondo-web
P. 143
Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax for DH-DPL
DPL cell lines (Figure 5A,B). In contrast, although the total protein levels of BCL2 were slightly decreased, the propor- tion of phosphorylated BCL2 was increased 6 h after expo- sure to venetoclax in BJAB cells (Figure 5C). Unexpectedly, MCL1 showed decreased expression levels in both Karpas231 and OCI-Ly8 cells within 3 h after exposure to venetoclax (Figure 5A,B). This phenomenon was not observed in the BJAB and SU-DHL10 lines (Figure 5C, D).
A
Furthermore, the expression of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) B56a, which has a critical role in dephosphorylation of BCL2,33 was decreased within 3 h after exposure to vene- toclax in both DH-DPL cell lines (Figure 5A,5B). The expres- sion levels of another regulatory subunit, PP2A B56δ,34 were unchanged in each cell line (Figure 5A-D). These results confirmed that venetoclax clearly changes the biological behavior of BCL2 and MCL1 in the two DH-DPL cell lines.
B
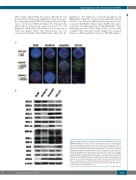
Figure 2. Characteristics of four germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-derived cell lines. (A) The four germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-derived cell lines have the MYC rearrangement. MYC is fused to IGH in BJAB, SU-DHL10, and OCI-Ly8 cells, while the IGH-BCL2 fusion was detected in SU-DHL10, Karpas231, and OCI-Ly8 cells. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses confirmed that SU-DHL10, Karpas231, and OCI-Ly8 are double-hit high grade B-cell lymphoma cell lines with MYC and BCL2 rearrange- ments. (B) Western blot analysis showed that the four lines express BCL6, MYC, BRD4, MCL1, BCL-xL, BIM, BAD, BAK, and BAX at a variety of levels. Despite the presence of the IGH-BCL2 fusion, SU-DHL10 cells failed to show BCL2 protein expression. In contrast, Karpas231 and OCI-Ly8 cells had abundant BCL2 pro- tein, a considerable part of which is phosphorylated (pBCL2) at serine 70. The results indicate that Karpas231 and OCI-Ly8 correspond to double-hit and dou- ble-protein-expression lymphoma cells.
haematologica | 2019; 104(7)
1421