Page 196 - 2019_04-Haematologica-web
P. 196
P. Durigutto et al.
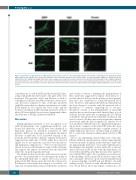
Figure 5. Deposition of β2glycoprotein I (β2GPI) and IgG on mesenteric vessels of rats treated with patients’ and controls’ serum IgG prior to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. The animals were treated with antibodies directed against domain 5 (D5), domain 1 (D1), or anti-β2GPI-negative (NHS) (10 mg/rat) before LPS administration (2.5 mg/kg body weight). Mesenteric tissue samples were analyzed for vascular deposition of β2GPI (left) and human IgG (center). Original magnifica- tion for immunofluorescence analysis 200x. Scale bar 50 mm. Thrombus formation in mesenteric vessels was monitored by intravital microscopy for 90 minutes and mesenteric tissue was collected at the end of the experiment. Thrombi formed in the vessels are indicated with arrows (right). Original magnification 100x. Scale bar 50 mm.
concentrations of soluble β2GPI and the residual IgG inter- acting with β2GPI directly bound to the plate wells were measured. The amount of IgG anti-D5 free to bind to solid-phase β2GPI after incubation with the soluble mole- cule decreased compared to that of the IgG incubated with BSA, particularly at a higher concentration of soluble β2GPI (Figure 6). In contrast, the level of IgG anti-D1 bound to solid-phase β2GPI following incubation with sol- uble β2GPI was slightly lower, but not significantly differ- ent from that of the IgG incubated with BSA.
Discussion
Antiphospholipid syndrome is now recognized as an antibody-dependent and complement-mediated syn- drome and antibodies to β2GPI have been identified as important players in thrombus formation in APS patients.10 Efforts are being made to determine the clinical relevance of antibodies to D1 and D4/5 domains of the molecule detected in these patients. Clinical studies have suggested that antibodies to D4/5, unlike those directed against D1, do not represent a risk factor for thrombosis and pregnancy complications.7,9,14 The in vivo data present- ed here focused on the thrombotic aspect of the syndrome and support the clinical observation that the anti-D4/5 antibodies are pathologically irrelevant.
The animal model used in this and in previous studies proved to be an invaluable tool to investigate the ability of the anti-β2GPI antibodies to induce blood clots in rats primed with LPS that provides the first hit, followed by the infusion of the antibodies acting as a second hit.10 As expected, all anti-D1 IgG promoted thrombus formation
and vascular occlusion, confirming the pathogenicity of these antibodies suggested by clinical observations. It is possible that LA detected in the plasma of these patients may have also contributed to anti-β2GPI-induced blood clots. However, although β2GPI antibody-dependent LA has been shown to correlate with the increased risk of thrombosis,13,14,36 evidence supporting the in vivo pro- thrombotic activity of LA independently of anti-β2GPI antibody has not yet been provided. Instead, there is good evidence that the antibodies recognizing the D1 domain of β2GPI are directly involved in thrombus formation and vessel occlusion. We have previously shown that a human monoclonal antibody that recognizes D1 induces blood clots and that a CH2-deleted non-complement fixing vari- ant molecule competes with anti-β2GPI antibodies from APS patients and prevents their pro-coagulant activity.27 A similar inhibitory effect was obtained using recombinant D1 to control the thrombus enhancement activity of aPL in mice.37
The in vivo experiments showed that none of the anti- D5 IgG exhibited a prothrombotic activity supporting the observations made in clinical studies that these antibodies are pathologically irrelevant.7,14 A possible explanation for this finding is the inability of these antibodies to interact with cell-bound β2GPI. In line with this hypothesis, we showed that anti-D5-positive IgG fractions were unable to react with β2GPI bound to CL-coated plates in vitro because of the shielding of D5 in the β2GPI molecule bound to the CL-coated plate. However, in rats treated with LPS (used to promote binding of β2GPI) and anti-D5 IgG, the mild staining for IgG observed on the endothelium of mesen- teric vessels did not allow any definite conclusions to be
824
haematologica | 2019; 104(4)