Page 144 - 2019_01-Haematologica-web
P. 144
K. Ohki et al.
Sanger sequencing of selected genes, including FBXW7, NLE, NOTCH1, PHF6, and PTEN, and combined these data with the results of WES. As shown in Table 2, muta- tions in NOTCH1 signaling pathway genes, including FBXW7, NLE, and NOTCH1, were detected in 4/16 patients. In addition, 8 and 1 of 16 patients exhibited mutations in PHF6 and PTEN, respectively.
Gene expression signature of MEF2D fusion-positive patients
We have microarray data of B-ALL as indicated in Online Supplementary Figure S1,11 and, in addition, we per- formed WTS to search for new fusion genes specifically among cases of B-other-ALL. To further assess the func-
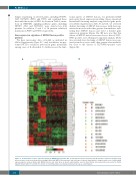
tional aspects of MEF2D fusions, we performed DNA microarray-based expression profiling. Upon supervised hierarchical clustering analysis using selected gene probe sets (Online Supplementary Table S7 and S8), we observed distinct clustering of MEF2D fusion cases, with clear sep- aration from cases with other genetic abnormalities, indi- cating that MEF2D fusion cases have a distinct gene expression signature (Figure 3A). Of note was that this cluster of MEF2D fusion cases was close to that of TCF3- PBX1-positive cases. Principal component analysis (PCA) also revealed clear clustering of MEF2D fusion cases sep- arate from those cases with other genetic abnormalities, but close to the cluster of TCF3-PBX1-positive cases (Figure 3B).
AB
Figure 3. Characteristics of gene expression profile in MEF2D-fusion-positive ALL. (A) Two-way hierarchical clustering and (B) principal component analysis (PCA) were performed on the microarray data, including B-ALLs with MEF2D fusion-positive and other types of genetic abnormalities, using the probe sets of differentially expressed genes between B-ALL with MEF2D fusions and other types of genetic abnormalities selected from filtered microarray probes (presented in Online Supplementary Tables S7 and S8). The results of clustering analysis are displayed using a heat map as a dendrogram.
134
haematologica | 2019; 104(1)