Page 27 - 2018_12-Haematologica-web
P. 27
VCAM-1/VLA-4
OPN/CD44
TGF-β
�VLA-4 Yes/No
�OPN Yes
�CD44v
� Jagged-1 TBI and Notch receptor
with limited autonomous Notch activation
Role of osteogenic niche in AML progression
serotonin synthesis in mice bearing MLL-AF9-induced AML attenuated disease burden.65 Conversely, using the same inducible model, Krause et al.8 showed that increas- ing osteoblastic activity through PTH activation aug- ments leukemic expansion in AML while inhibiting CML-like MPN.8 These contrasting data are, at least in part, due to the heterogeneity of osteolineage cells that are characterized differently across studies. However, these results may also reflect the intrinsic differences in osteoblast-leukemia interaction between acute and chronic myeloid malignancies.
Deregulated signaling network in the osteogenic niche offers promising therapeutic targets
In the past decade, huge strides forward have been made in AML induction therapy by combining chemo- and targeted therapies, yet this approach has offered lim- ited success in preventing disease recurrence. It is assumed that the osteogenic niche shields slow-cycling AML cells from cell cycle-dependent treatment just as it maintains HSC quiescence (Figure 3); however, that is just
the tip of the iceberg. The larger implication is that AML induces osteogenic dysfunction and disrupts the signaling network associated with the osteogenic niche (Table 1). This transformation of the niche could in turn fuel leukemia persistence and resistance to therapy. It is, therefore, critical to identify and target less visible threats underlying AML-osteogenic niche interactions to achieve more profound treatment efficacy.
Current approaches revolve mainly around disrupting BM homing axes, notably CXCL12/CXCR4. CXCR4 overexpression is common both at diagnosis72 and after chemotherapy,73 and correlates with poor prognosis in AML patients.74,75 CXCR4 inhibition prevents AML anchorage and promotes mobilization of leukemic stem/initiating cells (LSCs) out of the endosteal niche, thereby increasing their vulnerability to chemotherapy. Pre-clinical and clinical studies of CXCR4 antagonists have shown encouraging results, demonstrating that these agents not only sensitize AML cells to chemother- apy, but also reverse stroma-mediated antiapoptotic effects.76,77 Although the first generation of CXCR4
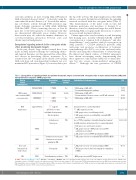
Table 1. Dysregulation of signaling network and potential therapeutic targets associated with osteogenic niche in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) progression.
Role in
normal hematopoiesis
HSC homing and retention in BM
osteogenic niche
HSC maintenance
Pathway
CXCL12/CXCR4
Deregulated feature
CXCR4
Prognostic marker?
Yes
Contribution to leukemogenesis
BM homing of AML LSCs Prosurvival/antiapoptotic pathways
Ref
73-77 81-84
Bone and
hematopoietic homeostasis
TBI
BM homing of AML LSCs
Stroma-mediated chemoresistance via NF-kB activation
BM homing of AML LSCs
Activation effect is context-dependent: AML expansion in vitro
AML progression (crosstalk unspecified)
AML progression in crosstalk with β-catenin/FoXO1 in osteoblasts
Activation via TBI fusion gene
Loss of TGF-β signaling is favorable though not required for AML initiation. Activation effect is context-dependent:
LSC quiescence and chemoresistance
AML progression & MPN progression via PTH activation in osteoblasts
AML progression via CTGF upregulation in MSCs
AML progression in crosstalk with TGF-β/CTGF in MSCs
�
AML progression via osteogenic priming in MSCs
MPN progression via deficient sympathetic stimulation of MSCs
Decrease; Mediate; TBI: to be investigated; HSC: hematopoietic stem cells; CXCL12: stromal derived factor-1; CXCR4 C-X-C:
89-92
88,112
Jagged-1/Notch
38,99,100,113
8,11,50,114
50,53
BMP
� Activation via fusion gene TBI Activation via osteogenic
priming by AML
49,101
SNS
In AML cells; In osteolineage cells;
chemokine receptor 4;VCAM-1:vascular cell adhesion protein-1;VLA-4:very late antigen-4;OPN:osteopontin;TGF-β:transforming growth factor β;BMP:bone morphogenetic protein; SNS: sympathetic nervous system; CCL3: chemokine ligand 3; BM: bone marrow; LSC: leukemic stem/initiating cells; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells; PTH: parathyroid hormone; CTGF: connective tissue growth factor.
haematologica | 2018; 103(12)
CCL3
Increase;
Neuropathy TBI
Proinflammatory cytokines TBI
� MPN progression via HSC displacement
1951
39