Page 28 - 2018_11-Haematologica-web
P. 28
M. Arock et al.
AB
CD
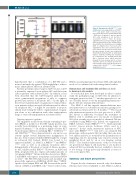
Figure 4. Engraftment of ROSAKIT D816V-Gluc cells in NSG mice. Increasing numbers of ROSAKIT D816V-Gluc cells (1x106, 5x106 or 10x106) were injected into the tail vein of NOD-SCID IL-2Rγ- /- (NSG) mice (3 groups; 6 mice per group) 24 h after irradiation at 2.5 Gy from a cesium-137 source.113 After 10 weeks, engraftment was assessed using (A) quanti- tative measurements of Gluc activity in plas- ma and (B) in vivo bioluminescence imaging (IVIS) on engrafted mice. Ten weeks after engraftment, mice were sacrificed and (C) bone marrow and (D) spleen sections from the three groups of mice were stained by immunohistochemistry with an anti-human tryptase antibody. Staining was visualized by a Histomouse Kit, showing human MC with a brownish stain, which massively invaded the bone marrow and to a lesser extent the spleen. (C) and (D) are from one representative mouse from the group inject- ed with 10x106 ROSAKIT D816V-Gluc cells. Original magnification, x100.
hypothesized that a combination of a KIT-TKI and a monoclonal antibody against CD52 might help to achieve major antineoplastic effects in advanced SM.
Another potential surface target is CD33. In fact, CD33 is invariably expressed on neoplastic MC and their stem cells in patients with advanced SM.95 In addition, it has been described that the CD33-targeted antibody-con- struct gemtuzumab-ozogamicin is able to suppress growth and survival of neoplastic MC.101 In the light of the revival of gemtuzumab-ozogamicin, its clinical effica- cy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and its effects on neoplastic MC,102 it might be reasonable to propose clinical trials testing the effects of gemtuzumab-ozogam- icin alone or in combination with other antineoplastic drugs or stem cell transplantation in advanced SM.
Targeting epigenetic regulators
The epigenetic reader bromodomain-containing 4 pro- tein (BRD4), a member of the BET family proteins, has recently been identified as a promising target in acute myeloid leukemia.103,104 In addition, highly selective BET bromodomain inhibitors, including JQ1,105 I-BET151,106,107 and I-BET762,106,108 have demonstrated in vitro and in vivo activity against several hematopoietic malignancies. It has also been evaluated whether BRD4 might be a target in advanced SM. Indeed, BRD4 was found to be expressed in HMC-1.1, HMC-1.2, ROSAKIT WT and ROSAK- IT D816V cells as well as in primary neoplastic MC.109 Independently of the grade or variant of disease, neoplas- tic MC exhibit nuclear BRD4.109 However, in ASM and MCL, neoplastic MC also express substantial amounts of cytoplasmic BRD4.109 In line with this observation, HMC- 1 and ROSA cells express cytoplasmic and nuclear BRD4 as well.109 The KIT-TKI midostaurin and dasatinib sup- pressed the expression of BRD4 in all MC lines.109 BRD4- specific short hairpin RNA and JQ1 decreased the prolif- eration of HMC-1 and ROSA cells.109 Based on these data,
BRD4 is a promising target in advanced SM, although this needs to be confirmed in forthcoming clinical studies.
Human mast cell leukemia-like cell lines as tools to develop in vivo models
In vivo models have been developed in order to under- stand the pathophysiology of SM better. In addition to transgenic mouse models,110,111 another approach is to cre- ate a SM-like disease in vivo by transplanting human neo- plastic MC into immunodeficient mice.
The HMC-1 cell line engrafts immunodeficient mice after intravenous or subcutaneous injection, giving rise to subcutaneous tumors after 2 to 5 months.11, 112 The reason why intravenous injection does not give rise to a MCL- like disease is unknown, but limits the usefulness of HMC-1 cells to establish an in vivo model of advanced SM. More recently, an in vivo model of advanced SM was established using ROSA cells. Indeed, we engineered a ROSA subclone, termed ROSAKIT D816V-Gluc, which naturally secretes Gaussia princeps luciferase (Gluc), used as a reporter.113 In this study, intravenous injection of NSG mice with ROSAKIT D816V-Gluc cells led to an advanced SM phenotype, with neoplastic MC invading the bone mar- row, spleen and liver, as testified by the quantification of engrafting cells by measuring Gluc reporter activity in peripheral blood and by an in vivo imaging system (IVIS).113 The detailed characteristics of this in vivo model are presented in Figure 4. All in all, this in vivo model of advanced SM is potentially the best available to date for in vivo testing of drugs previously identified as active in vitro on neoplastic MC.
Summary and future perspectives
Despite decades of intensive research, only a few human MC lines have been established to date: HMC-1, LAD-2,
1768
haematologica | 2018; 103(11)