Page 36 - Haematologica August 2018
P. 36
P. Shyamsunder et al. Results
CEBPE predominantly binds at intergenic and intronic regions and regulates gene expression
We previously identified genome-wide CEBPE binding sites in unfractionated mouse bone marrow cells using
chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq).21 Total bone marrow cells are composed of approximately 40-50% of mature granulocytes that express high levels of CEBPE. Further analysis of ChIP- seq data revealed that the overall binding pattern of CEBPE was similar to other CEBP factors, with increased binding
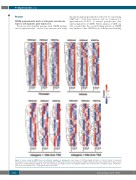
Figure 2. Genes bound by CEBPE have an activation signature in granulocytes. Heat maps of ChIP-Seq signal intensities of histone marks in long term hematopoetic stem cells (LT-HSC), common myeloid progenitors (CMP), granulocyte-monocyte progenitor (GMP) and granulocytes (Gr) populations for genes whose expression is downregulated in CEBPE KO cells and categorised according to location of binding of CEBPE to the promoter, intron, intergenic region <10kb and > 10kb of the nearest gene TSS.22 *in the figure represents Card10.
1272
haematologica | 2018; 103(8)