Page 27 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 27
REVIEW ARTICLE - ITP: diagnosis and second-line treatment J.B. Bussel and C.A. Garcia
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2026
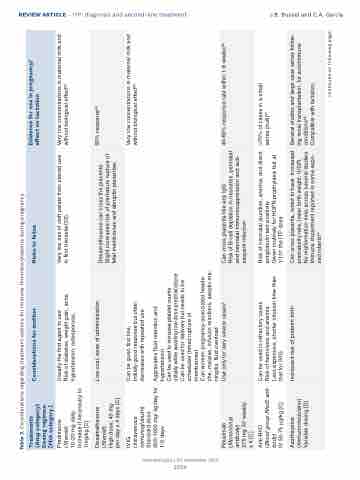
Table 3. Considerations regarding treatment options for immune thrombocytopenia during pregnancy.
Treatments (Drug category) Dosing regimen [FDA category ]
Considerations for mother
Risks to fetus
Evidence for use in pregnancy/ effect on lactation
Prednisone
(Steroid)
10-20 mg daily. Increase if necessary to 1mg/kg [C]
Usually the first agent to use
Risk of diabetes, weight gain, acne, hypertension, osteoporosis,
Very low risk of cleft palate from steroid use in first trimester(53).
Very low concentrations in maternal milk and without biological effect90
Dexamethasone (Steroid)
High dose, 40 mg per day x 4 days [C]
Low cost, ease of administration
Dexamethasone can cross the placenta. Slight increased risk of premature rupture of fetal membranes and abruptio placentae.
50% response64
IVIG
(Intravenous immunoglobulin) Standard dose 400-1000 mg/ kg/day for 1-5 days
Can be given first line,
Initially good response but often decreases with repeated use
Very low concentrations in maternal milk and without biological effect90
Rituximab (Monoclonal antibody)
375 mg IV/ weekly x 4 [C]
Aggravates fluid retention and
hypertension
Can be used to increase platelet counts initially while awaiting low dose prednis(ol)one Can be used for delivery but needs to be scheduled (timed rupture of
membranes)
Can worsen pregnancy-associated heada- che, malaise, infusion reactions, aseptic me- ningitis, fluid overload
Use only for very severe cases5
Can cross placenta like any IgG
Risk of B-cell depletion in neonates, perinatal and neonatal immunosuppression and sub- sequent infection
40-60% response rate within 1-8 weeks66
Anti-RhD
(Blood group RhoD anti- body)
IV 50-75 μg/kg [C]
Can be used in refractory cases
Risk of hemolysis and anemia
Less expensive, shorter infusion time than that for IVIG
Risk of neonatal jaundice, anemia, and direct antiglobulin test positivity
Given routinely for HDFN prophylaxis but at 1/10th the ITP dose
>70% of cases in a small series (n=8)67
Azathioprine (Immunomodulator) Variable dosing [D]
Increased risk of preterm birth
Can cross placenta, noted to have increased prematurity rate, lower birth weight, IUGR. No malformation risks across several studies Immune impairment reported in some expo- sed infants69
Several studies and large case series follow- ing renal transplantation, for autoimmune conditions68
Compatible with lactation
continued on following page.