Page 268 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 268
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
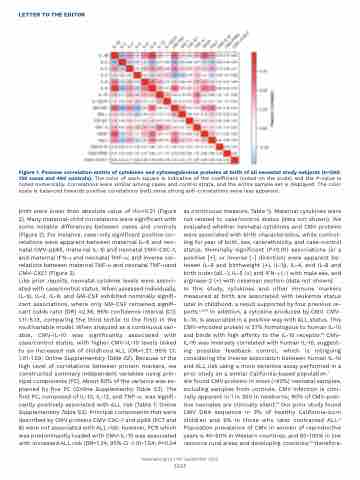
Figure 1. Pearson correlation matrix of cytokines and cytomegalovirus proteins at birth of all neonatal study subjects (n=590: 130 cases and 460 controls). The color of each square is indicative of the coefficient (noted on the scale) and the P-value is noted numerically. Correlations were similar among cases and control strata, and the entire sample set is displayed. The color scale is balanced towards positive correlations (red) since strong anti-correlations were less apparent.
birth were lower than absolute value of rho=0.21 (Figure 2). Many maternal-child correlations were significant with some notable differences between cases and controls (Figure 2). For instance, case-only significant positive cor- relations were apparent between maternal IL-6 and neo- natal CMV-pp65, maternal IL-1b and neonatal CMV-CXC-1, and maternal IFN-γ and neonatal TNF-a; and inverse cor- relations between maternal TNF-a and neonatal TNF-aand CMV-CXC1 (Figure 2).
Like prior reports, neonatal cytokine levels were associ- ated with case/control status. When assessed individually, IL-1b, IL-2, IL-8, and GM-CSF exhibited nominally signifi- cant associations, where only GM-CSF remained signifi- cant (odds ratio [OR] =2.38, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.11-5.13, comparing the third tertile to the first) in the multivariable model. When analyzed as a continuous vari- able, CMV-IL-10 was significantly associated with case/control status, with higher CMV-IL-10 levels linked to an increased risk of childhood ALL (OR=1.27, 95% CI: 1.01-1.59; Online Supplementary Table S2). Because of the high level of correlations between protein markers, we constructed summary independent variables using prin- cipal components (PC). About 60% of the variance was ex- plained by five PC (Online Supplementry Table S3). The first PC, composed of IL-10, IL-12, and TNF-a, was signifi- cantly positively associated with ALL risk (Table 1; Online Supplementary Table S3). Principal components that were described by CMV proteins CMV-CXC-1 and pp65 (PC7 and 8) were not associated with ALL risk; however, PC9 which was predominantly loaded with CMV-IL-10 was associated with increased ALL risk (OR=1.24, 95% CI :1.01-1.54; P=0.04
as continuous measure, Table 1). Maternal cytokines were not related to case/control status (data not shown). We evaluated whether neonatal cytokines and CMV proteins were associated with birth characteristics, while control- ling for year of birth, sex, race/ethnicity, and case-control status. Nominally significant (P<0.01) associations (in a positive [+], or inverse [-] direction) were apparent be- tween IL-6 and birthweight (+), IL-1b, IL-4, and IL-8 and birth order (all -), IL-5 (+) and IFN-γ (-) with male sex, and arginase-2 (+) with cesarean section (data not shown).
In this study, cytokines and other immune markers measured at birth are associated with leukemia status later in childhood, a result supported by four previous re- ports.1,3,4,7 In addition, a cytokine produced by CMV, CMV- IL-10, is associated in a positive way with ALL status. This CMV-encoded protein is 27% homologous to human IL-10 and binds with high affinity to the IL-10 receptor.12 CMV- IL-10 was inversely correlated with human IL-10, suggest- ing possible feedback control, which is intriguing considering the inverse association between human IL-10 and ALL risk using a more sensitive assay performed in a prior study on a similar California-based population.1
We found CMV proteins in most (~90%) neonatal samples, including samples from controls. CMV infection is clini- cally apparent in 1 in 300 in newborns; 90% of CMV-posi- tive neonates are clinically silent.13 Our prior study found CMV DNA sequence in 3% of healthy California-born children and 9% in those who later contracted ALL.2 Population prevalence of CMV in women of reproductive years is 40-60% in Western countries, and 80-100% in low resource rural areas and developing countries;14 therefore,
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2267