Page 160 - Haematologica May 2022
P. 160
J.N. Gustine et al.
AB
CD
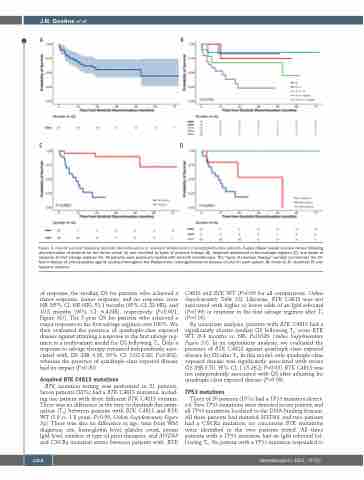
Figure 3. Overall survival following ibrutinib discontinuation in resistant Waldenström macroglobulinemia patients. Kaplan-Meier overall survival curves following discontinuation of ibrutinib for the entire cohort (A) and stratified by types of previous therapy (B), response attainment to first salvage regimen (C), and depth of
response to first salvage regimen (D). All patients were previously treated with ibrutinib monotherapy. The “types of previous therapy” variable summarizes the dif- ferent classes of anti-neoplastic agents received throughout the Waldenström macroglobulinemia disease course for each patient. IB: ibrutinib; R: rituximab; PI: pro- teasome inhibitor.
of response, the median OS for patients who achieved a major response, minor response, and no response were NR (95% CI: NR-NR), 51.1 months (95% CI: 23-NR), and 10.8 months (95% CI: 6.4-NR), respectively (P<0.001; Figure 3D). The 5-year OS for patients who achieved a major response to the first salvage regimen was 100%. We then evaluated the presence of quadruple-class exposed disease against attaining a response to the first salvage reg- imen in a multivariate model for OS following T0. Only a response to salvage therapy remained independently asso- ciated with OS (HR 0.08, 95% CI: 0.02-0.38; P=0.002), whereas the presence of quadruple-class exposed disease had no impact (P=0.20).
Acquired BTK C481S mutations
BTK mutation testing was performed in 21 patients.
Seven patients (33%) had a BTK C481S mutation, includ- ing one patient with three different BTK C481S variants. There was no difference in the time to ibrutinib discontin- uation (T0) between patients with BTK C481S and BTK WT (1.9 vs. 1.8 years; P=0.50; Online Supplementary Figure S4). There was also no difference in age, time from WM diagnosis, sex, hemoglobin level, platelet count, serum IgM level, number or type of prior therapies, and MYD88 and CXCR4 mutation status between patients with BTK
C481S and BTK WT (P>0.05 for all comparisons; Online Supplementary Table S3). Likewise, BTK C481S was not associated with higher or lower odds of an IgM rebound (P=0.99) or response to the first salvage regimen after T0 (P=0.16).
By univariate analysis, patients with BTK C481S had a significantly shorter median OS following T0 versus BTK WT (6.4 months vs. NR; P=0.026; Online Supplementary Figure S5). In an exploratory analysis, we evaluated the presence of BTK C481S against quadruple-class exposed disease for OS after T0. In this model, only quadruple-class exposed disease was significantly associated with worse OS (HR 5.50, 95% CI: 1.15-26.2; P=0.03). BTK C481S was not independently associated with OS after adjusting for quadruple-class exposed disease (P=0.09).
TP53 mutations
Three of 20 patients (15%) had a TP53 mutation detect-
ed. Two TP53 mutations were detected in one patient, and all TP53 mutations localized to the DNA-binding domain. All three patients had mutated MYD88, and two patients had a CXCR4 mutation; no concurrent BTK mutations were identified in the two patients tested. All three patients with a TP53 mutation had an IgM rebound fol- lowing T0. No patient with a TP53 mutation responded to
1168
haematologica | 2022; 107(5)