Page 128 - 2022_03-Haematologica-web
P. 128
V. Madan et al.
Supplementary Figure; Online Supplementary Table S4), sug- gesting that ZRSR1 can also regulate their splicing. Comparison of Zrsr2 single KO with Zrsr2/Zrsr1 double- deficient Lin−Kit+ BM cells showed two subclasses of retained introns in Zrsr2/Zrsr1 double deficient cells. The first subclass comprises those introns which are retained in Zrsr2 KO cells, and their DMSI increases significantly in double-deficient cells; while the second category includes introns which are retained only when both ZRSR1 and ZRSR2 are lacking (Online Supplementary Figure S7B).
Retention of U12-type introns in the Zrsr2/Zrsr1 dou- ble-deficient cells was validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of 10 introns, which illustrated a modest effect of loss of ZRSR2 alone on splicing of U12- type introns, while concomitant deficiency of ZRSR1 and
ZRSR2 significantly enhanced intron retention compared to either WT or single KO cells (Figure 4C).
Further, in order to verify the compensatory role of murine ZRSR1 in splicing of U12-type introns, CRISPR/Cas9 technique was used to generate myeloid cells (32D) lacking either one or both ZRSR proteins. Firstly, the whole Zrsr2 coding sequence was deleted using two guide RNA targeting exons 2 and 11 of Zrsr2 gene (Online Supplementary Figure S8A and B). Two single cell clones of Zrsr2 KO 32D cells were generated (Online Supplementary Figure S8B and C). Subsequently, we delet- ed the N-terminus portion of the Zrsr1 gene to generate single or double KO 32D cells (Online Supplementary Figure S8A, B, D and E). qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated aber- rant retention of U12-type introns in Zrsr1/Zrsr2 double-
ABC
DE
F
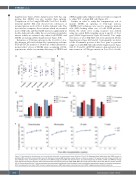
Figure 2. Hematopoietic development and reconstitution potential are unperturbed upon deletion of Zrsr2. (A) Peripheral blood white blood cell (WBC) counts in wild-type (WT) and Zrsr2 knockout (KO) mice. (B) Total bone marrow (BM) leukocyte counts (femurs + tibias) in young (7-10 weeks) and old (≥1-year old) WT and Zrsr2-deficient mice. (C) Proportion of LSK cells in the BM of young and old WT and Zrsr2 KO mice. (D and E) Frequencies of LT-HSC, ST-HSC and MPP (D) (Young mice: five WT and five KO; Old mice: five WT and three KO) and myeloid precursors (CMP, GMP, MEP) (E) (Young mice: five WT and five KO; Old mice: six WT and four KO). (F) Donor-derived B cells, T cells, granulocytes and monocytes in peripheral blood of recipient mice in competitive repopulation assays (six recipient mice/group). HSC: hematopoietic stem cells; CMP: common myeloid precursors; GMP: granulocyte monocyte precursors; MEP: megakaryocyte erythroid precursors.
684
haematologica | 2022; 107(3)