Page 23 - 2022_02-Haematologica-web
P. 23
GE-based biomarkers in CML
haematologica | 2022; 107(2)
365
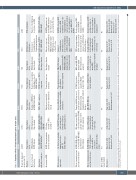
Table 3. Functional effects of frequently mutated genes in blast crisis.
Frequency: diagnosis/ progression (%)
2.6/18.3
6.1/16.0
9.7/15.1
0.9/8.6
0/8.4
0.9/6.7
2.3/4.5
DNA methylation
Function
Transcription factor
Transcription factor
Transcriptional repression
Transcriptional co-repressor
Transcription factor
Methylcytosine dioxygenase
Mode of action and interactions
DNA binding via RUNT domain.
DNA binding via zinc finger domain.
Regulator of H3K27me3 & H2AK119ub1 marks
Represses transcription by binding to class II HDAC & CTBP1
DNA binding via zinc finger domain
Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
Transfer of methyl group to cytosines on DNA
Interactions
with other complexes
P300,CBP,PRC1,NuRD, SWI/SNF, MLL/TrxG
HDAC1,HDAC2,CHD3, CHD4, PRC2, CtBP1, SWI/SNF
PRC2,BAP1complexes
PCGF1,thecorePRC1.1 component
FOG1throughN-terminal Zinc finger domain
2-HG,vitaminC,OGT, WT1, VPRBP, IDAX
PRC2,EVI1,ISGF3,AP2a, ZEB1, HDAC1
Aberration in CML
RUNT domain mutations deletions and fusions
Deletions-
exon D4–7 (IK6), exon D2–7
Majority are frameshift and nonsense mutations in exon 12
Frameshift, nonsense mutations
Zinc finger domain variants
Missense, nonsense
and frameshift mutations TET2 mutations may be CHIP-related or a part
of the Ph+ clone
DNMT3A mutations are mostly CHIP mutations since they are also present in the Ph- clone
Effects on gene expression
Up: Interferon signaling, immune molecules, pDC- TF.
Down: DNA repair
Up: JAK-STAT signaling, self-renewal genes. Down: B-cell lineage and DNA repair genes
Increased Brd4 occupancy and chromatin accessibility around genes
Transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin.
Other targets unknown
CML L359V mutant inhibits
transactivation by PU.1. GATA2 MDS and AML mutants have altered transactivation activity
Impaired 5-methylcytosine hydroxylation and decreased methylation at CpG sites in myeloid cancers with mutant TET2
DNMT3A-deficient HSC show loss of DNA methylation at the edge of hypomethylated canyon regions enriched for self-renewal genes such as MEIS1, EVI1, HOXA9
Effect of mutant protein/ gene knock out in vitro
RUNX1 H78Q orV91 fs-ter94 in 32D-BCR-ABL1 model blocked differentiation
IK6 expression in CD34+
cellsisolatedfromCP-CML proliferation,anddecreased
BCORL1 depletion increased the re-plating capacity of Runx1- depleted Lin− cells
MDS and AML GATA2 mutants inhibit differentiation and apoptosis
TET2 silencing in human CD34+ cells increased the monocytic lineage at the expense of erythroid and lymphoid lineages
Nearly a third of CHIP- related DNMT3A mutations reduce protein stability
Effect of mutant protein/ gene knock out in vivo
RUNX1 H78Q or V91fs-ter94 mutants
Ikaros DNA binding domain inactivation in early pre-B cells leads to ALL
AML, MPN, MDS-like diseases
Effect of CML BCORL1 variants unknown
GATA2 deficiency has been recognized as a major MDS predisposition syndrome in humans
Conditional TET2 loss in the hematopoietic compartment leads
to increased stem cell self-renewal
Dnmt3a ablation in HSC predisposes mice to develop a spectrum of myeloid and lymphoid malignancies
Effect on CML variant studied
Yes
Zhao et al., 2012
Yes
Joshi et al., 2014
Yes
No
Pagan et al., 2007
No
Zhang et al., 2009
No
Kim et al., 2017
No
Mayle et al., 2015
References
Awad et al., 2020 Branford et al., 2018
Beer et al., 2015
Yang et al., 2018
Katoh, 2013 Balasubramani et al., 2015
Wong et al., 2016
Branford et al., 2018
Pronier et al., 2011 Crusio et al., 2011
Hervouet et al., 2018 Huang et al., 2018 Kim et al., 2017 Branford et al., 2018
RUNX1
IKZF1
ASXL1
BCORL1
GATA2
TET2
DNMT3A
induced a BC or accelerated phase-like phenotype in mice
patients enhances their in vitro expansion
Truncated ASXL1 increased differentiation along
megakaryocyte and erythroid lineages
HDAC: histone deacetylases; CML: chronic myeloid leukemia; CHIP: clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential; MDS: myelodysplastic syndrome; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; HSC: hematopoietic stem cell; CP: chronic phase; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; MPN: myeloproliferative neoplasm.