Page 317 - 2022_01-Haematologica-web
P. 317
Letters to the Editor
expression (Figure 1B). We also confirmed that the drug efficiently targets the Wnt pathway by using a luciferase reporter vector in HCT116, a colorectal cancer cell line that shows constitutive activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 1C). We also confirmed Wnt targeting by WNT974 in primary AML samples (Online Supplemental Table S1 for patients’ details). As shown in Figure 1D, WNT974 decreased mRNA expression of the MYC gene, which is considered one of the main oncogenes driven by
A
abnormal Wnt/b-catenin signaling. We also observed a similar reduction in mRNA expression of other Wnt tar- get genes such as CTNNB1 and GSK3B after WNT974 treatment of primary AML samples (Online Supplementary Figure S1A).
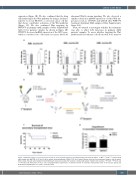
Next, we wanted to investigate whether the treatment was able to affect LSC functions in primary AML patients’ samples. To assess whether targeting the Wnt pathway affects leukemia cell self-renewal, bone marrow
B
CD
Figure 3. WNT974 activity in a primary murine model of acute myeloid leukemia. (A) Colony-forming unit assay of CD117+ m MllPTD/WT/Flt3ITD/WT bone marrow cells treated with WNT974 at 0.5 and 1 mM or vehicle (dimethylsulfoxide, DMSO 0.1%) for 2 weeks. Results from the first scoring are shown in the left panel. After scoring, the cells were replated in fresh Methocult media and scored after another 2 weeks (right panel). Student t-test analysis: *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. (B) Flow chart of the in vivo re-transplantations experiment. (C) Overall survival of secondary transplanted mice (n=5 mice per group). (D) Evaluation of engraftment at 1 month. *P<0.05 (t-test).
haematologica | 2022; 107(1)
309