Page 88 - 2021_10-Haematologica-web
P. 88
L. Grassi et al.
A
B
C
D
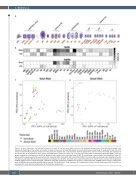
Figure 1. Dataset description and principal component analysis of total and small RNA expression. (A) Graphical representation of the cell types included in the dataset. (B) Heatmaps of the number of samples for each cell type used for total RNA (above) and small RNA (below) sequencing. (C) Scatterplot of the first (PC1) versus the second (PC2) principal component of the expression of genes with a log expression estimate greater than zero in at least one sample. (D) Scatterplot of PC1 versus PC2 of the expression of the various small RNA with a unique read count >10 in at least one sample. MSC: mesenchymal stem cells; BOEC: blood out- growth endothelial cell progenitors; HUVEC (R): resting human umbilical vein endothelial cells; HUVEC (P): proliferating human umbilical vein endothelial cells; PLT: platelets; MK: megakaryocytes; EB: erythroblast; BAS: basophils; EOS: eosinophils; NEU: neutrophils; MONO: monocytes; M0: macrophages; M1: lipopolysaccharide- activated macrophages; M2: alternatively activated macrophages; DC: dendritic cells; CD4 naïve: naïve CD4 lymphocytes; CD4CM: central memory CD4 lymphocytes; CD4EM: effector memory CD4 lymphocytes; CD8 naïve: naive CD8 lymphocytes; CD8CM: central memory CD8 lymphocytes; CD8EM: effector memory CD8 lympho- cytes; CD8TDEM: terminally differentiated effector memory CD8 lymphocytes; T reg: regulatory CD4 lymphocytes; B naïve: naive B lymphocytes; BM: memory B lym- phocytes; BCS: class switch B lymphocytes; NK: natural killer lymphocytes.
2616
haematologica | 2021; 106(10)