Page 45 - 2021_10-Haematologica-web
P. 45
Targeting PKC and BET induces differentiation of AML
AB
CE
F
D
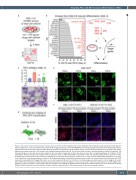
Figure 4. H4 induces leukemic differentiation through activation of PKC. (A) Primary AML-3 cells were treated with 176 compounds (5 mM, 0.5 mM, and 0.05 mM) with defined targets alone and in combination with compound H4 (10 μM). (B) Inhibition of the RAF/MEK/ERK and JNK signaling pathway inhibited H4-induced differentiation together with inhibition of kinases upstream (PKC, RTK, SYK, and LYN) and downstream of the pathway (GLS1). Compounds were omitted from the analysis if their toxicity reduced cell numbers more than 75% relative to the number following treatment with H4. The data are shown as mean ± standard deviation of technical replicates. The schematic diagram on the right shows kinase targets of the most potent compounds and how they relate to each other in signaling pathways. (C) Inhibition of PKC (GF109203X 4 mM) confirmed that compound H4 (10 mM) was unable to differentiate AML-3 cells without intact PKC signaling. Representative examples of May- Grünwald Giemsa staining are shown (scale bars represents 10 mm) and the data are mean ± standard error of mean from two independent experiments (**P<0.01, ns not significant, using one-way analysis of variance). (D) Schematic illustration of the PKC translocation assay, which is an essential step in PKC activation. HEK-293T cells were transfected with GFP-tagged PKCα, bII, e, and d, and treated with 40 mM of H4 for 20 min. Confocal images were taken every 5 s. (E) H4 triggers the translo- cation of PKC from the cytosol to membranes. Representative examples of confocal images at 0 and 3 min are shown. Scale bars represent 20 mm. (F) H4 triggers phos- phorylaton of PKCα and PKCe in primary AML-3 cells and the AML cell line MOLM-13. Representative examples of confocal images at 30 min of treatment are shown (MOLM-13 PKCα 40 mM of H4 and the rest with 10 mM). Scale bars represent 40 mm. PKC: protein kinase C; AML: acute myeloid leukemia.
haematologica | 2021; 106(10)
2573