Page 204 - 2021_10-Haematologica-web
P. 204
A. D'Alessandro et al.
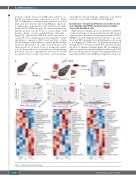
products, which decreased in KO mice, whereas car- boxylic acids increased (2-oxoglutarate, itaconate - Figure 3D). Comparably to kidneys, similar increases in several fatty acids were noted in livers from KO mice (myristole- ic, palmitoleic, dodecanedioic and tetradecenoic acids), though PCMT1 KO livers were also characterized by sig- nificant decreases in the levels of several amino acids (leucine, lysine, cysteine, phenylalanine, threonine – Figure 3E). Spleens from KO mice had lower levels of several 18 carbon-chained fatty acids (similarly to brains and kidneys, opposite to RBC, heart and liver – Figure 3F). In summary, while different organs each had distinct metabolic phenotypes, all organs from KO mice were characterized by (i) lower levels of methionine utiliza- tion, (ii) decreased pools of glutathione and glutathione precursors, and (iii) compensatory activation of the PPP (as inferred from steady state levels of intermediates,
A
especially in brain and spleen), suggestive of an altered capacity to cope with oxidant stress in KO mice.
Exacerbation of metabolic differences in red blood cells from wild-type and PCMT1 knockout mice by oxidant stress with diamide in vitro
While the above analysis showed a clear effect of PCMT1 on the metabolome, it was performed in a baseline state of oxidative stress. In order to test the hypothesis that PCMT1 KO RBC would be impaired in their response to an oxida- tive insult, RBC were incubated with diamide in vitro for up to 6 h (Figure 4A). While the overall metabolic impact of deleting PCMT1 was greater in the RBC metabolome than the effect of diamide treatment (Figure 4B), we identified a subset of metabolites that had a higher baseline level in WT RBC and which increased further following diamide treat- ment only in WT but not in KO mice (Figure 4C – blue box).
BCD
Figure 3. Continued on the following page.
2732
haematologica | 2021; 106(10)