Page 119 - 2021_10-Haematologica-web
P. 119
Vitronectin stabilizes leukocyte adhesion
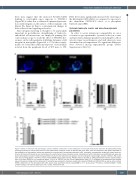
these data suggest that the increased ICAM-1/CD54 binding to neutrophils upon exposure to VN-PAI-1 (Figure 5B) is rather due to enhanced/optimized presenta- tion of b2 integrins on the surface of these immune cells (Figure 5A; Figure 6) than to conformational changes in these adhesion and signaling molecules.
Since integrin clustering is thought to be particularly important in postadhesion strengthening of leukocyte- endothelial cell interactions, we employed spinning disc confocal microscopy to study the effect of VN-PAI-1 het- eromers on the cell membrane trafficking dynamics of b2 integrins in neutrophils (Figure 6A to C). In these experi- ments, we found that additional exposure of neutrophils isolated from the peripheral blood of WT mice to VN-
A
B
PAI-1 heteromers significantly increased the clustering of the b2 integrin CD11a/LFA-1 as compared to exposure to the chemokine CXCL1/KC alone, or to phosphate buffered saline (PBS).
Systemic leukocyte counts and microhemodynamic parameters
In order to assure intergroup comparability in our in vivo microscopy experiments, systemic leukocyte counts and microhemodynamic parameters including blood flow velocity, inner vessel diameter, and wall shear rate were determined in each experiment. No significant differences were detected among experimental groups (Online Supplementary Table S1).
C
Figure 4. Effect of vitronectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 heteromers on the stabilization of neutrophil intravascular adhesion. (A) Using confocal laser scanning microscopy on tissue whole mounts of the postischemic cremaster muscle of wild-type (WT) mice, PAI-1 (blue) and vitronectin (VN) (green) deposited on the endothelium of postcapillary venules was detected to co-localize with intravascularly adherent Ly-6G+ neutrophils, representative images are shown (scale bar: 10 mm). (B) Using multi-channel in vivo microscopy on the postischemic mouse cremaster muscle, interactions of Ly-6G+ neutrophils and endothelial cells were ana- lyzed in postcapillary venules. Panels show quantitative results for short adhesion and adhesion time of neutrophils in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)-defi- cient mice receiving vehicle or the PAI-1 mutant proteins PAI-RR (active stable mutant), PAI-QR (unable to bind VN), or CPAI (proteolytically inactive; mean±standard error of the mean [SEM] for n=4 animals per group; *P<0.05 vs. PAI-RR). See also Online Supplementary Table S1. (C) Employing an autoperfused flow chamber assay, intravascular rolling and firm adherence of neutrophils was analyzed in chambers coated with E-selectin/CD62E and ICAM-1/CD54 as well as with or without VN-PAI-1 heteromers or the chemokine CXCL1/KC, panels show quantitative results (mean±SEM for n=7–14 per group; *P<0.05 vs. E-selectin/CD62E + ICAM- 1/CD54 coating). I/R: ischemia-reperfusion; min: muntes, FOV: field of view.
haematologica | 2021; 106(10)
2647