Page 245 - 2021_09-Haematologica-web
P. 245
CASE REPORT
Clinical genomic profiling of novel grey zone lymphoma paired lesions with sequential central nervous system involvement in two adolescent patients
Grey zone lymphoma (GZL), defined as B-cell lym- phoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) and classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) (BCL-U-IND) is a rare diagnos-
tic entity.1-3 Synchronous GZL, LBCL and cHL occurring simultaneously in the same patient, and sequential GZL, LBCL preceding or following a diagnosis of cHL, are even less common.4 We identified two adolescent patients, a 17 year-old male (17M, case #1) and 16 year-old female (16F, case #2), who were diagnosed with stage IV nodular sclerosis cHL (NS-cHL) with primary mediastinal location and subsequent central nervous system (CNS) LBCL. Copy-number alterations were assessed using Affymetrix OncoScan® microarray analysis, and targeted next-gener-
haematologica | 2021; 106(9)
2533
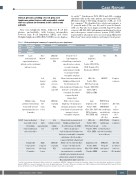
Table 1. Clinicopathological summary of sequential grey zone lymphomas.
Case/ age (yr)/ sex
Presentation (time after initial diagnosis)
Biopsy site
Bone Marrow^
Left internal jugular LN
Frontal lobe brain lesion
Diagnosis
LBCL-like synchronous GZL
cHL, nodular sclerosis subtype, stage IVA
LBCL-like sequential GZL
cHL, nodular sclerosis subtype, stage IVB
LBCL-like sequential GZL
Morphology
Focal sheets of
large lymphoma
cells with large round nuclei, smooth nuclear contours,
vesicular chromatin,
and prominent centrally located nucleoli with eosinophilic cytoplasm Characteristic mononucleated Hodgkin and binucleated Reed-Sternberg cells
Immunophenotype
Large lymphoma
cells: Positive: CD19, CD79a, CD45; Negative: CD3, Cytokeratin, TdT, CD30.
HRS cells: Positive: CD30, CD15, Pax-5 (weak);
Therapy
NA
ABVE-PC
POG9917 Arm A bridged to MMUD BMT
Outcome (follow-up period)
NA
Complete remission
Alive with no evidence of disease
(81.7 months) Complete remission
Alive with no evidence of disease (13.5 months)
Large mediastinal and supraclavicular masses with spleen, liver, abdominal and bone lesions
#1/17/M
Multiple supra-
and infra-tentorial brain lesions with extensive leptomeningeal diseases (6 months)
histiocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils; the nodules separated by thick collagen band
Diffuse sheets of large lymphoma cells having open chromatin, prominent centrally located nucleoli and a moderate
amount of clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm.
CD79a, LMP-1, EBER and EMA
Large lymphoma cells: Positive: CD45,
#2/16/F Large mediastinal mass with cervical
LN, multiple bilateral pulmonary and renal nodules
Solitary right temporal lobe brain lesion (7 months)
Deep right supraclavicular LN
Right temporal lobe brain lesion
Characteristic mononucleated Hodgkin and binucleated Reed-Sternberg cells (HRS) with focal aggregates
in the background of lymphocytes, histiocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, and plasma cells; the nodules separated by thick collagen band Diffuse sheets of intermediate
to large cells with smooth
to irregular nuclear contour, inconspicuous to occasionally centrally located prominent nucleoli and moderate amount of cytoplasm. Occasional mitotic figures present
(450 cGy). ABVE-PC with radiotherapy
to the mediastinal mass and slow-responding areas of disease
inthebackgroundoflymphocytes, Negative:CD45,CD20,
CD20, CD30, PAX-5 with conditioning
CD79a; Negative: CD15, EBER, ALK
and total body irradiation
HRS cells: Positive: CD30, CD15, Pax-5 (weak); Negative: CD45, CD20, EBER
Lymphoma cells: Positive: CD45, CD20, CD30, MUM1; Negative: EBER
ANHL1131 Group C1 and surgical excision
^Outside bone marrow with limited slides reviewed as consultation. ABVE-PC: adriamycin, bleomycin, vincristine sulfate, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, cyclophos- phamide; BMT: bone marrow transplant; cHL: classic Hodgkin lymphoma; F: female; GZL: grey zone lymphoma; HRS: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg; LBCL: large B-cell lym- phoma; LN: lymph node; M: male; MMUD: mismatched unrelated donor; NA: not applicable.