Page 76 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 76
J.C. Gutjahr et al.
A
B Ci
Cii Di
Dii E
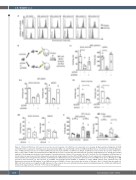
Figure 1. CD44 and CD49d are both expressed on acute myeloid leukemia cells; CD44 has a predominant role in homing. (A) Representative histograms of CD44 and CD49d surface expression of primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and the AML cell line OCI-AML3. (B) Mononuclear cells from bone marrow (BM) aspi- rates of AML patients pretreated or not with αCD44 antibody clone 515 (αCD44) or αCD49d clone HP2/1 (αCD49d) were injected into the tail veins of NSG mice. After 3 h the number of AML cells that had homed to BM and spleen of the recipients was determined by flow cytometry using human-specific αCD44 and αCD49d antibodies. The homing rate was defined as the number of measured leukemic cells per 106 measured cells per 106 injected cells. (Ci) Homing rate to BM and spleen 3 h after injection was measured in five independent experiments using samples from five different AML patients. In each experiment, technical duplicates were per- formed and they were averaged for the analysis. (Cii) Homing rate to BM and spleen was measured 3 h after injection of OCI-AML3 (n=2). (Di + ii) Homing rate to BM and spleen was measured 3 h after injection of OCI-AML3 cells transduced with shCD44 or shCD49d or control shRNA (shCont) (n=4, unpaired t-test). (E) Mononuclear cells from the BM aspirate of one AML patient and OCI-AML3 cells were injected into the tail veins of NSG mice. After 3 h and 3 days the number of AML cells that had homed or engrafted to BM and spleen of the recipient mice was determined by flow cytometry using human-specific αCD44 and αCD49d anti- bodies (n=4, unpaired t-test). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ns: not significant.
2104
haematologica | 2021; 106(8)