Page 182 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 182
S. Warsi et al.
Discussion
A large body of work from a variety of model systems has established a critical role for BMP signaling during early development.5-7 Studies performed in vitro indicate that BMP signaling continues to function in the regulation of HSC beyond development.19,20,36 However, SMAD1 and SMAD5 are dispensable for adult HSC function in mice, leading to the conclusion that BMP play a limited role, if
AB
any, in adult HSC regulation in vivo.21,22 The SMAD circuit- ry is undoubtedly the best characterized pathway down- stream of BMP, but the lack of HSC phenotype in mice deficient of SMAD1 and SMAD5 does not automatically rule out a role for BMP signaling in adult HSC, as non- SMAD pathways can also be activated by BMP.24,25 The fact that BMPR-II is highly expressed in LT-HSC has left a gap in knowledge between the BMP circuitry and its function in adult HSC in vivo.23
CD
EF
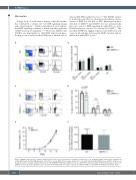
Figure 4. BMPR-II deficient mice exhibit normal apoptosis and cell cycle parameters of primitive hematopoietic cells. (A) Representative fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of LSK-SLAM/Annexin V stain of bone marrow (BM). (B) Percentage of Annexin V+ cells within indicated LSK-SLAM subsets of BM of adult mice at steady state (n=5). (C) Representative FACS plots of LSK-SLAM/Ki67/DAPI stain of BM. (D) Cell cycle distribution in percent within long-term hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSC) (n=9-10). (E) In vitro growth of c-kit+ cells (n=3). (F) Homing assay. Percentage of Lin-/Sca1+/CD150+/CD45.2+ cells in BM of transplanted recipients (n=5).
2210
haematologica | 2021; 106(8)