Page 105 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 105
Bile acids reduce GvHD and preserve the GvL effect
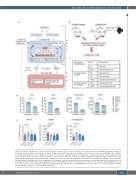
Figure 1. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation induces changes in bile acid levels and bile acid receptor expression. (A) Simplified schematic overview of bile acid metabolism and the enterohepatic circulation. (B) Experimental flow for metabolomic profiling of the bile acid pool from untreated BALB/c mice and mice developing graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). (C) Overview of the bile acids quantified by liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry. (D) Quantification of the bile acid composition in liver, ileum, ileal contents and serum of untreated mice and on day 7 after bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Data were pooled from five indi- vidual mice per group and are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean for each metabolite. P-values were calculated for the total bile acid pool using the two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test; ns: not significant. (E) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of the mRNA expression of the bile acid recep- tors Nr1h4 (encodes for the FXR protein) and Gpbar1 (encodes for the TGR5 protein) in the small intestine of untreated mice and mice developing GvHD. Data are pooled from n=10 mice in the untreated, GvHD d7 and GvHD d14 groups and n=5 mice in the GvHD day 4 group. The P-values were calculated using the ordinary one-way ANOVA test with correction for multiple comparisons.
D
E
AB
C
haematologica | 2021; 106(8)
2133