Page 244 - 2021_05-Haematologica-web
P. 244
1464
Letters to the Editor
formation. Strikingly, however, this temporal restriction can be overcome by enforced CK2 expression, leading to high penetrance of leukemia development. Although CK2α overexpression alone cannot induce leukemia, it promotes the survival of lymphocytes. Hence, it is likely that MYC activation at a later stage of development induces apoptosis in lymphocytes that is overcome by
A
CK2 overexpression, enabling the rapid induction of leukemia in these fish.
As CK2 inhibition with the selective and potent inhibitor, CX-4945, exhibits anti-tumor activities,7 CX- 4945 has been included in clinical testing to treat hema- tological malignancies (clinicaltrials.gov. Identifier: NCT01199718) and solid cancers (clinicaltrials.gov
B
C
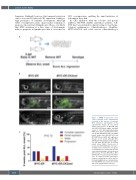
Figure 3. CK2α overexpression alone cannot maintain acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the absence of aberrant MYC activation. (A) Diagram of the experimental design. (B, top panel) Thymic fluorescence in MYC-ER (left) and MYC-ER;CK2αwt (right) zebrafish raised in 129 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4HT) for 5 weeks showing tumor initia- tion in MYC-ER;CK2αwt fish. (B, middle panel) shows both MYC-ER (left) and MYC-ER;CK2αwt (right) with aggressive disease at 11 weeks although MYC- ER;CK2αwt fish developed more aggres- sive ALL than MYC-ER fish. (B, bottom panel) shows thymic fluorescence 4 weeks after 4HT withdrawal. One repre- sentative fish is shown for each group. (C) Zebrafish were classified by the indi- cated tumor phenotype at 8 weeks post 4HT removal (P=0.13; MYC-ER vs. MYC- ER;CK2αwt; n=11 per group). The differ- ence in observed tumor phenotypes between each group as a whole was sta- tistically insignificant, as calculated by a two-way ANOVA test. Scale bars =1 mm. ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
haematologica | 2021; 106(5)