Page 45 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 45
Novel PBD inhibit NF-κB in hematologic cancers
NIK fusion protein. U266 cells exhibit a TRAF3 mutation causing stabilization of wild-type NIK protein.23,24 Both cell lines were treated for 4 h with up to 20 nM of each agent and the relative change in nuclear p65 (RelA), p50, p52 and RelB DNA binding was determined as a function of the untreated control. Levels of c-Rel were not evaluat- ed in this study as JJN3 cells show very low levels of this subunit relative to the dominant canonical subunits p65 and p50. In JJN3 cells, all the PBD showed significant inhi-
A
B
bition of p65, p50 and Rel B but no significant reduction in p52 (Figure 4A). In contrast, U266 cells showed a sig- nificant reduction in the nuclear DNA binding of all four subunits (Figure 4B).
Transcriptional effects of DC-1-170 and DC-1-192 on JJN3 cells
As predicted, RNA-sequencing analysis of DC-1-170 and DC-1-192 revealed a dominant inhibitory effect on
C
D
E
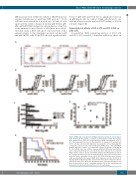
Figure 2. PBD induce apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines in a dose-depen- dent manner. (A) An example of annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) bivariate plots obtained from JJN3 cells treated with increasing concentrations of DC-1- 92. A dose-dependent increase in the proportion of annexin V+/PI- and annexin V+/PI+ cells was observed. (B) Sigmoidal dose-response curves illustrating the comparative effects of each compound in U266, OPM2, H929, JJN3 and MM1.S multiple myeloma cell lines. (C) Comparative analysis of the three lead PBD in the five multiple myeloma cell lines revealed significant differential sensitivity to each compound and between each cell line but DC-1-192 was the most potent PBD in all five cell lines. (D) The relationship between the NF-κB index of each of
value. (E) In order to inves- tigate the in vivo antitumor effects of DC-1-192, NOD/SCID mice were systemi- cally inoculated with the human RPMI 8226 myeloma cell line. DC-1-192 (1 mg/kg) significantly prolonged the survival of the mice when compared to that of untreated control mice. All in vitro experiments were performed in triplicate and data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The in vivo experiment was
the cell lines and their respective mean DC-1-192 LD performed in treated and untreated mice (n=7 for each group).
50
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)
961