Page 148 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 148
Y. Shi et al.
ABC
DEF
G
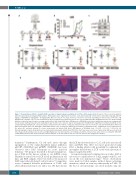
Figure 7. Dexamethasone (DEX) + dasatinib (DAS) synergize to impair leukemia engraftment in a Phase II-like murine trial. (A) Layout of the in vivo trial using ten different patient-derived xenograft (PDX) samples. PDX samples were engrafted into four mice each and treated with control vehicle (Ctrl), DEX (1 mg/kg), DAS (35 mg/kg) or DEX+DAS (1 mg/kg DEX + 35 mg/kg DAS). Mice were dosed once daily, 5 times per week, for 2-3 weeks depending on clinical status of the mice. (B) Engraftment of hCD45+ cells (%) was determined weekly in peripheral blood derived from four mice injected with PDX L809. Engraftment levels are shown starting from day of injection (day 0) in mice receiving control vehicle (Ctrl, black), DAS (blue), DEX (green), or DEX+DAS (red). Vertical dotted lines indicate the treatment win- dow (3 weeks) starting on day 46 and completing on day 64. Mice were culled on day 72 and analyzed for hCD45/hCD7 engraftment. (C) Western blotting of total and phosphorylated lymphocyte cell-specific kinase (LCK) protein levels of whole cell lysates derived from the spleens of four mice injected with PDX L809 under four different treatment arms (Ctrl, DAS, DEX or DEX+DAS) relative to the housekeeper GAPDH. (D-F) Summary of final human CD7+ engraftment (%) in peripheral blood (D), spleen (E), and bone marrow (F) of mice treated with Ctrl (black), DAS (blue), DEX (green), or DEX+DAS (red). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (G) Photomicrographs of whole brain-skull sections stained with Hematoxylin & Eosin from PDX L809. (Left) Low power scout view of whole brain with area shown in all other images marked by black box. (Centre and right) High power view (x20 objective) of meninges around the central venous sinus in mice receiving Ctrl, DAS, DEX or DEX+DAS treatment. Red arrows mark the leukemic infiltrate. Scale bar marks 1 mm on scout view and 100 mm on high power images.
transition.29 Furthermore, G1 cell cycle arrest, through upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21CIP1 (CDKN1A) and p27KIP1 (CDKN1B), has been observed after DAS treatment in acute myeloid leukemia.30 We propose that LCK is the predominant tar- get of DAS in this disease setting, as our shRNA screen identified a critical role for LCK in cell proliferation in cell lines and PDX samples. Moreover, LCK is the proposed DAS target when blocking T-cell activation.21 Competitive assays confirmed defective proliferation of T-ALL cells after LCK knockdown in vitro and in vivo. We have shown
that LCK knockdown leads to G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in cell lines and PDX. This effect was more pronounced using DAS, a finding which could potentially be explained by incomplete knockdown of LCK or the wide spectrum of kinases targeted by DAS.
As reported earlier and confirmed in our studies, DAS is cytotoxic to a small subset of T-ALL samples with IC50 val- ues in the low nanomolar range.31 These observations were made in T-ALL samples without kinase activating mutations, which are seen very infrequently in T-ALL. To the best of our knowledge, our cohort includes only one
1064
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)