Page 85 - 2021_02-Haematologica-web
P. 85
C-FGF23 peptide alleviates hypoferremia
ABC
DEF
GH
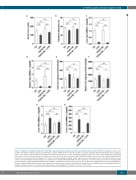
Figure 6. Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) signaling alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hypoferremia. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were treat- ed with C-tail FGF23 (1 mg/kg, indicated as FGF23 BL) or vehicle (HEPES buffer) for 8 hours (h). Mice were then challenged with LPS (intraperitoneal 50 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.9% NaCl) for 4 h. (A) Serum iron and (B) serum transferrin saturation. (C and D) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) for ferroportin (Fpn) expression in (C) liver and (D) spleen. (E and F) Iron content in (E) liver and (F) spleen. (G and H) qRT-PCR for hepatic expression of (G) ferritin H and (H) lipocalin (Lcn2). Data are expressed as fold change (2-DDCt) relative to housekeeping gene Gapdh. Samples were measured in duplicates (n=5-7 per group). Data are repre- sented as mean+standard deviation. All data were analyzed for normality with Shapiro-Wilk test and equivalence of variance using Levene’s test. For samples with normal distribution, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test was performed (B, E, F, and G). When the samples did not show normal distribution, they were aligned in RANK transformation, and confirmed for normality. As the samples showed normal distribution, two-way ANOVA was performed with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (A, C, D, and H). Ctl: control (vehicle), ns: not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
haematologica | 2021; 106(2)
399