Page 38 - 2021_02-Haematologica-web
P. 38
F. Bernardi and G. Mariani et al.
logical and clinical information currently available. That is, the relationship between the reduced levels of FVII/bleeding tendency and high levels of FVII/ risk of cardiovascular disease. We will particularly focus on dis- tinctive features of the FVII protein and F7 gene (Table 1) as well as on open issues (Table 2).
Genetics and biochemical aspects
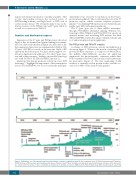
Expression of the F7 gene and FVII protein is shown in Figure 2. Key biochemical and genetic findings are summa- rized on a historical time line in Figure 1A, and some of the key unanswered questions are summarized in Table 2. The F7 gene9 (12.8 KB) is located on chromosome 13q34, 2 KB apart from the homologous F10 gene, which suggests evo- lution by duplication. In addition to F10, the F7 gene struc- ture and coding sequence19 displays a noticeable homology also with F9 (factor IX, FIX) and PROC (protein C).
Mutations that disrupt promoter activity in severe FVII deficiency20,21 highlight the importance of the transcription factors SP1 and HNF4α, but do not sustain the androgen-
A
dependent rescue observed for mutations in the F9 pro- moter in hemophilia B. The evolutionary history of the F7 promoter region, which contains frequent polymor- phisms22,23 modulating FVII expression (see dedicated para- graph), may differ in human populations.
The F7 gene gives rise to three mRNA transcripts12 through FVII mRNA alternative splicing. Whereas two transcripts (NM_019616.4 and NM_000131.4) encode an identical mature and circulating FVII protein, the third (NM_001267554.1) lacks the amino terminal domains and is of unknown physiological significance.
The FVII protein and FVIIa-TF complex
A scheme of FVII activation, activity and inhibition is shown in Figure 3. Whereas the mature circulating FVII protein (50 KDa) sequence19 is composed of 406 residues, the mRNA (NM_019616.4) encodes 60 additional aminoacids, the pre-propeptide sequences which drive FVII biosynthesis/secretion and are removed by intracellu- lar proteolysis (Figure 2). The first numbering (1-406 residues) is currently used in protein studies, and the sec- ond one (1-466 codons) in molecular genetics.
B
Figure 1. Publications over 70 years and some key achievements related to coagulation factor VII. (A) Coagulation factor VII (FVII) biochemistry and F7 genetics. (B) FVII deficiency, FVII level associated cardiovascular disease, FVII levels and F7 gene: N: number of publications reported in Pubmed. Only some of the discoveries are referenced in the text due to space constraints. A complete list is available on request. GWAS: Genome Wide Analysis Study; NGS: next-generation sequencing.
352
haematologica | 2021; 106(2)