Page 31 - 2021_02-Haematologica-web
P. 31
Inherited platelet function disorders
Genotype
Identification of pathogenic variants for HPS involves ten subtypes (HPS1-10) and ten genes: AP3B1, AP3D1, BLOC1S3 encoding for BLOS-3, BLOC1S6 encoding for pallidin, DTNBP1 encoding for dysbindin, HPS1, HPS3- 6.69-71 All of the genes encode subunits organized in four multi-subunit protein complexes, named biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex (BLOC)-1, -2 and -3 and the adaptor protein-3 complex (AP-3).67-71 The HPS phenotype is related to the BLOC complex affected (Figure 4). BLOC-1 consists of eight subunits of which dysbindin (HPS7), BLOS-3 (HPS8) and pallidin (HPS9) are mutated in rare patients with a mild or absent bleeding diathesis and variable hypopigmentation. HPS3, HPS5, and HPS6 are subunits of BLOC-2; mutations in these genes are more frequent than those in the BLOC-1 and affected individuals have a mild clinical phenotype with a bleeding syndrome and hypopigmentation only. HPS1 and HPS4 are subunits of BLOC-3; mutations in these cases are predominantly associated with severe manifestations (severe oculocutaneous albinism, pulmonary fibrosis, granulomatous colitis). BLOC-3 defects are the most fre- quent form of HPS with p.His497Glnfs*90 in HPS1, the
first HPS mutation to be discovered; this form is common in Puerto Rico.67 The AP-3 complex has four subunits with AP3B1 encoding β3A mutated in HPS-2 and AP3D1 encod- ing AP-3d mutated in HPS-10. AP-3 is important for dense granule biogenesis and protein delivery to the forming granule (e.g., the serotonin transporter, VMAT2).69-72 Variants of AP3B1 are said to cause HPS type II. Interestingly, Enders et al. detected a homozygous non- sense mutation in AP3B1 together with a heterozygous bystander RAB27A mutation in a child with bleeding, albinism, developmental delay and a susceptibility to infections; HPS type II was diagnosed rather than Griscelli syndrome as would indicate a RAB27A mutation.72 HPS-10 is a very rare form of HPS characterized by partial oculo- cutaneous albinism, bleeding, neutropenia and immunod- eficiency. Defective protein disulfide isomerase release from platelets and endothelial cells in HPS contributes to the impaired thrombus formation and could represent a novel target for antithrombotic drugs.73
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
The most important clinical problem of patients with Chediak-Higashi syndrome is immunodeficiency with life-
AB
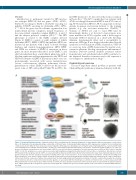
Figure 4. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Syndromic platelet defect resulting from the abnormal biogenesis of dense granules with an autosomal recessive inheri- tance. (A) Summarizes the genotype/phenotype relationship of different types of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) regrouped according to the four multi-protein complexes involved in different steps of lysosome-related organelle (LRO) biogenesis including vesicle formation and/or trafficking: BLOC1, 2 and 3 and AP-3 with each containing several subunits. Variants in HPS 7, 8 and 9 are causal in BLOC1 but with mild clinical consequences. For BLOC2, variants in HPS 3, 5 or 6 give syn- dromes of moderate severity; they are rare but a variant of HPS 3 occurs in Puerto Rican communities. The most frequent causes of HPS are BLOC3 defects (variants in HPS 1 or 4). The syndromes are severe and are associated with lung fibrosis and gastro-intestinal defects; in Puerto Rico a community is affected by a common HPS1 variant. In the last group, defects of AP-3 are associated with neutropenia and infections. (B) A scheme illustrates the major steps of granule biogenesis. Dense granules may derive from the endolysosomal system, including either early or late endosomes. As secretory granules the membrane constituents including mem- brane transporters come from the Golgi complex. A network of interconnected and functionally distinct tubular subdomains transports their cargoes along micro- tubule tracks from the endosomes. Tubules ferry contents from the trans-Golgi-network and the plasma membrane to the LRO, a system that requires the coordina- tion of numerous effectors. Components stored in dense granules or associated with their membranes are shown. (C) Platelets from a control and a patient with HPS3 examined by electron microscopy as whole mounts are shown. The dense granules observed in controls as black spots are absent from the patient’s platelet. AP-3: adaptor protein-3; BLOC: biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex; LRO: lysosome-related organelle; OCA: oculocutaneous albinism; MVB: multivesic- ular body.
C
haematologica | 2021; 106(2)
345