Page 177 - 2021_02-Haematologica-web
P. 177
PAI-1 blockade eliminates leukemia stem cells
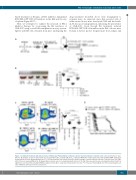
bined treatment of IM plus a PAI-1 inhibitor diminished BCR/ABL-GFP+ LSK cell numbers in the BM and the size of spleen (Figure 6B-C).
Next, we attempted to validate the rationale of PAI-1 inhibitor therapy for overcoming the IM resistance of CML-LSC using a serial BM transplantation assay system. Spleen and BM cells obtained from mice undergoing the
drug treatment described above were transplanted to recipient mice. As expected, mice that received cells of saline-treated donor mice developed CML and died with- in 20 days post transplantation, indicating the persistence of CML-LSC. Even though IM treatment reduced BCR/ABL-GFP+ LSK cell numbers in the BM of donor mice by half, it did not protect recipient mice from relapse and
A
B
CD
Figure 6. Combined treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitor plus PAI-1 inhibitor eradicates chronic myeloid leukemia - leukemic stem cells. (A) Schema for expe- riments. (B) Analysis of spleens taken from mice treated with saline, imatinib (IM) alone, or IM plus TM5614 in combination either with anti-MT1-MMP antibody or isotype-matched control immunoglobulin (n=6-7). (C) Representative flow cytometric profiles and percentage of chronic myeloid leukemia - leukemic stem cells (CML- LSC) in the bone marrow (BM) (n=9). (D) Kaplan Meier survival curves of serially transplanted mice (n=10-14). Data represent means ± standard devaition. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney unpaired t-test (B) or a log-rank non-parametric test (D). P<0.001, by a Kruskal-Wallis test. PAI-1: plasminogen acti- vator inhibitor-1; GFP: green fluorescent protein.
haematologica | 2021; 106(2)
491